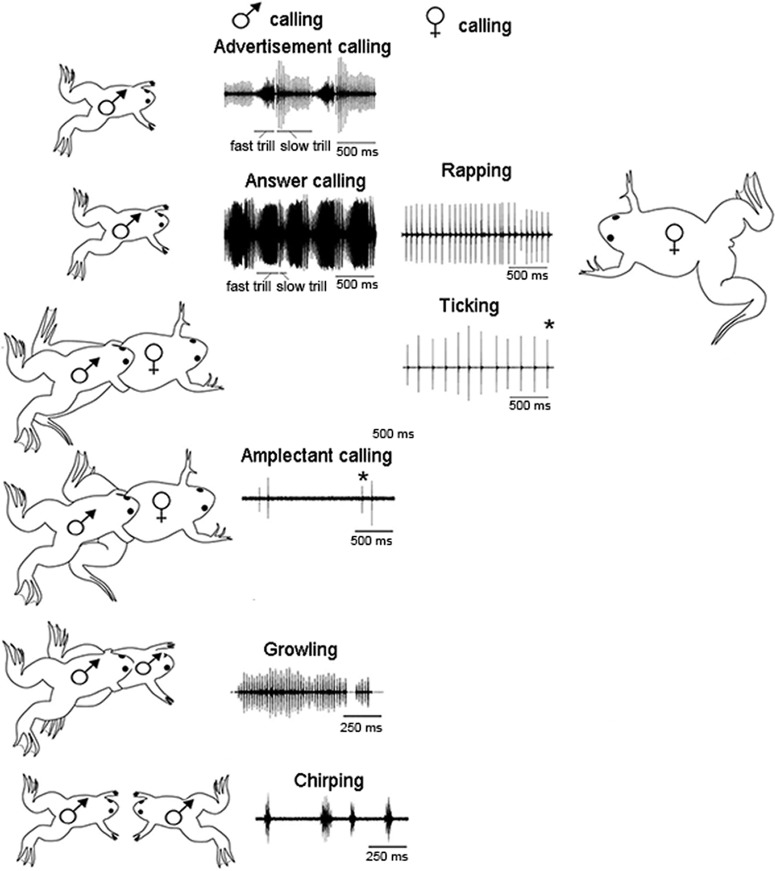
Figure 1.
The vocal repertoire of X. laevis is sexually differentiated and specific to social context. The male advertisement call consists of individual sound pulses* at fast (60 pps) and slow (30 pps) rates. Males produce advertisement calls when alone or with conspecifics. When oviposition is imminent, females produce a rapid (16 pps) series of sound pulses known as rapping. Rapping serves as an acoustic aphrodisiac and stimulates male answer calling. When clasped, sexually unreceptive females extend their hind legs and produce the slower ticking call (6 pps). A male clasping another frog, male or female, produces the amplectant call. A clasped male responds with growling. During the social interactions that precede one male vocally suppressing another, males produce the chirping call. Modified from Zornik and Kelley, 2011. pps: pulses per second.