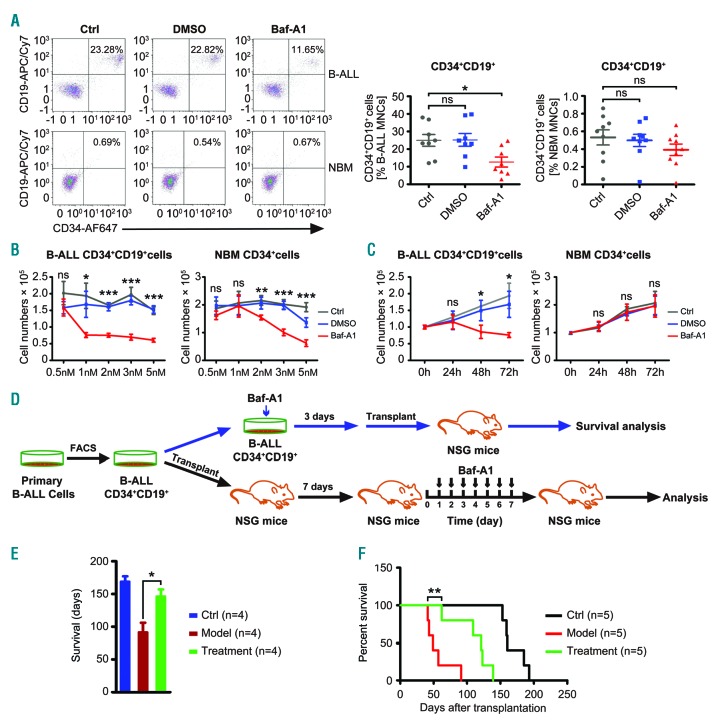
Figure 1.
Low-dose bafilomycin A1 extends the lifespan of humanized leukemia mice engrafted with CD34+CD19+cells derived from patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of the frequency of CD34+CD19+ cells in primary mononuclear cells from eight patients (ALL#1-8) with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and normal bone marrow (NBM) mononuclear cells from nine healthy donors after 1 nm bafilomycin A1 treatment. (B) Reduction of primary B-ALL CD34+CD19+ cells by bafilomycin A1 is dose-dependent. Left, ALL patients (#9-14), n=6; right, normal hematopoietic cells from healthy donors, n=6. (C) Reduction of primary B-ALL CD34+CD19+ cells is time-dependent. Left, 24 h and 48 h n=3, ALL#12,15,16; 72 h n=6, ALL#9-14; right, 24 h and 48 h n=3, 72 h n=6, NBM CD34+ cells from healthy donors. (D) Schematic experimental design for NSG mice engrafted with B-ALL CD34+CD19+ samples after bafilomycin A1 treatment either ex vivo (n=4, ALL#14,17-19) or in vivo (n=5, ALL#20-24). (E) Ex vivo treatment with 1 nm bafilomycin A1 prolonged the lifespan of the NSG mice engrafted with B-ALL CD34CD19 cells (n=4, ALL#14,17-19). (F) Survival curve reflecting time to lethal leukemia burden in NSG mice injected with 1-5x106 B-ALL CD34+CD19+ cells, and 7 days later, treated with vehicle or bafilomycin A1 (0.1 mg/kg) (n=5/group, ALL#20-24). Ctrl: control; DMSO: dimethylsulfoxide; Baf-A1: bafilomycin A1.