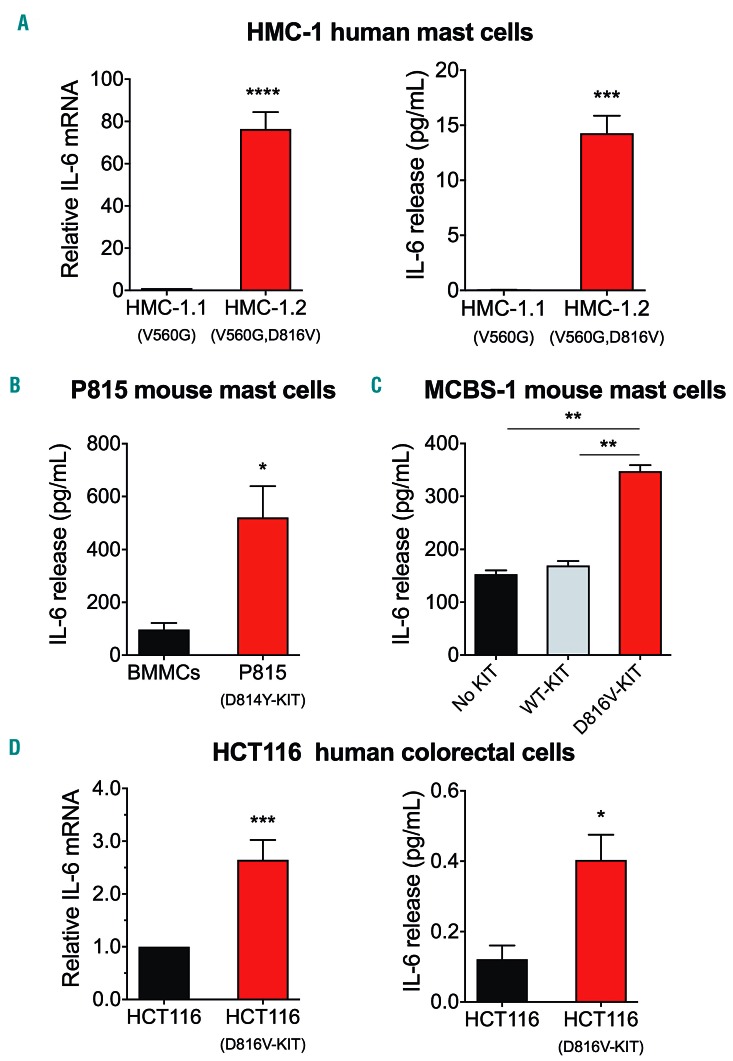
Figure 2.
Cells with D816V-KIT constitu-tively express and release IL-6. (A) IL-6 mRNA expression (left) and IL-6 released into the media (right) by the mastocytosis cell lines HMC-1.1 (with V560G) and HMC-1.2 (with V560G and D816V) after 2 hours (h) in serum-free media. (B and C) Comparison of IL-6 released into the media by the mouse P815 mastocytoma mast cell line (with D814Y-KIT) compared to normal murine bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMC) (B), and by the murine mast cell line MCBS-1 (which lacks c-Kit) transfected with human KIT or D816V-KIT compared to MCBS-1 transfected with vector alone (C). (D) Comparison of IL-6 mRNA expression (left) and IL-6 released into the media (right) by the human colorectal carcinoma cell line HCT116 expressing or not D816V-KIT. HCT116 cells were stimulated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and ionomycin overnight. IL-6 mRNA expression was determined by quantitative-real-time polymerase chain reaction (q-RT-PCR) and relative expression was calculated in relationship to the expression of GAPDH using the DCt method and expressed as fold change compared to HMC-1.1 (A, left), or the HCT116 parental cell line (D). All data (A-D) are the results of three independent experiments done in triplicates. *P=0.01; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001.