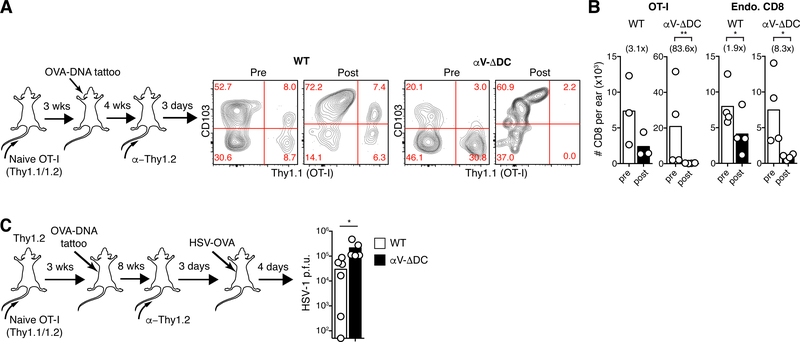
Fig. 3. Residual eTRM cells formed in absence of DC-expressed αV-integrins are unstable and provide reduced antiviral protection.
(A-B) 106 CD44lo CD62Lhi naive OT-I cells were adoptively transferred into αV-ΔDC or WT recipients. Three weeks later, animals were vaccinated by ear tattoo with OVA-encoding plasmid DNA. After an additional 4 weeks, circulating T cells were depleted with α-Thy1.2 mAbs, and then, 3 d later, the expression of CD103 (A) and absolute numbers in skin of total CD8+ T cells (B) derived from OT-I (left) or from polyclonal endogenous cells (right) were determined. Number in parentheses indicate fold decrease in αV-ΔDC mice Data are means and replicates and representative of two independent experiments. (C) Mice were seeded with OT-I eTRM cells as in (A), but in the flank. Eight weeks later, circulating T cells were depleted, and an additional 3 d later, animals were exposed at vaccinated skin sites with HSV-OVA. Four days later, local viral titers were determined in skin. Data are medians and biological replicates, each replicate representing the mean of a technical triplicate, and representative of two independent experiments. */**: p<0.05/p<0.01 (Two-tailed paired Student’s t-tests in (B), *: p<0.05 (Mann–Whitney U test in (C)).