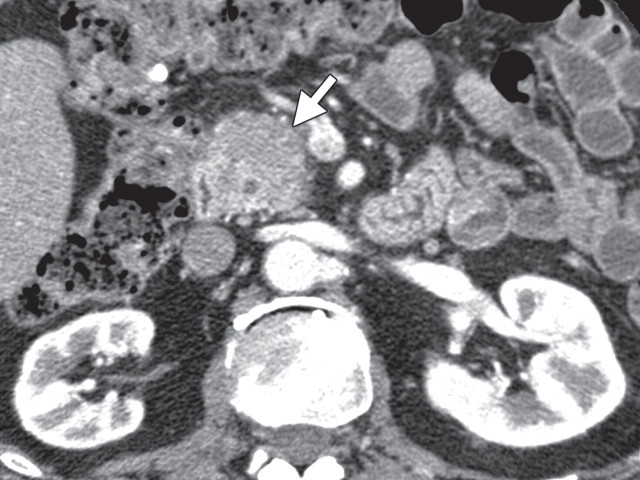
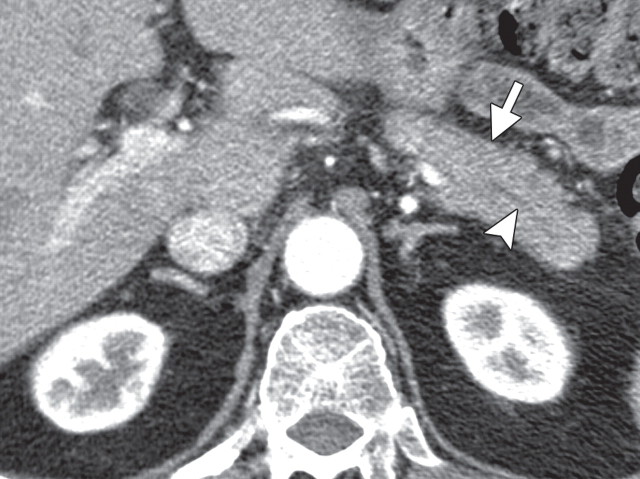
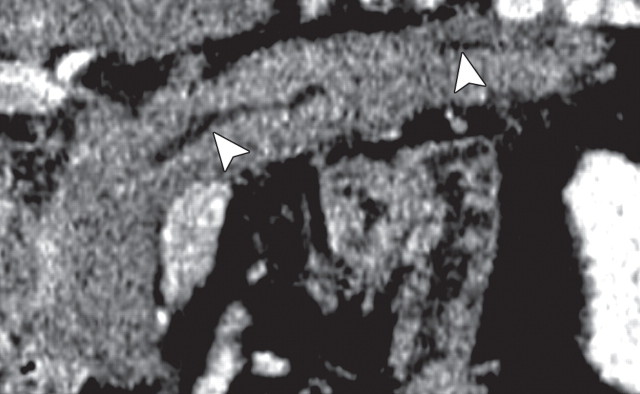
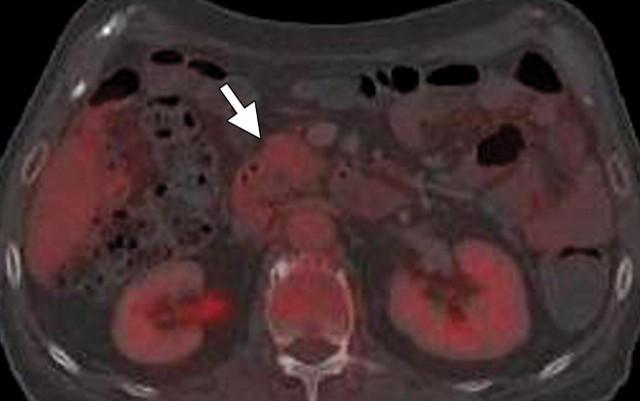
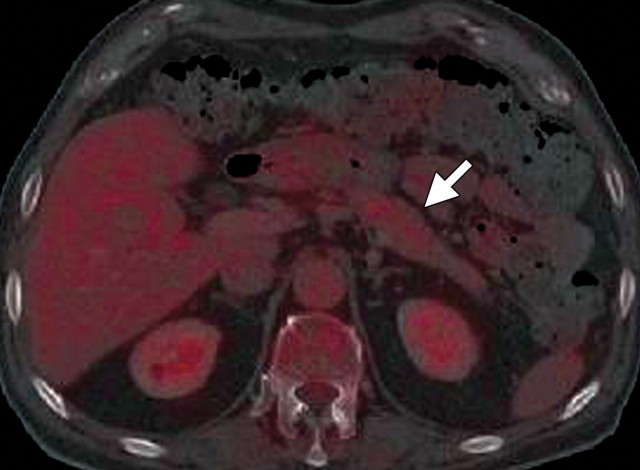
AIP in a 77-year-old man experiencing abdominal pain, weight loss, and jaundice. (a) Axial contrast-enhanced multidetector CT image shows a hypoattenuating mass in the pancreatic head (arrow). (b, c) Axial contrast-enhanced multidetector (b) and coronal reformatted (c) CT images show the pancreatic body and tail, which are slightly enlarged (arrow in b). Partial obliteration of the pancreatic outline and mild prominence of the main pancreatic duct (arrowheads) are also seen, findings indicative of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. (d, e) Axial PET/CT images show mild to moderate heterogeneous FDG uptake within the pancreatic head (arrow in d) and the rest of the body and tail (arrow in e), a finding indicative of a diffuse low-grade process, such as AIP. Serum CA 19-9 levels were not elevated, and endoscopic US–guided biopsy results were inconclusive. Corticosteroid therapy resulted in a favorable clinical and radiologic response.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.