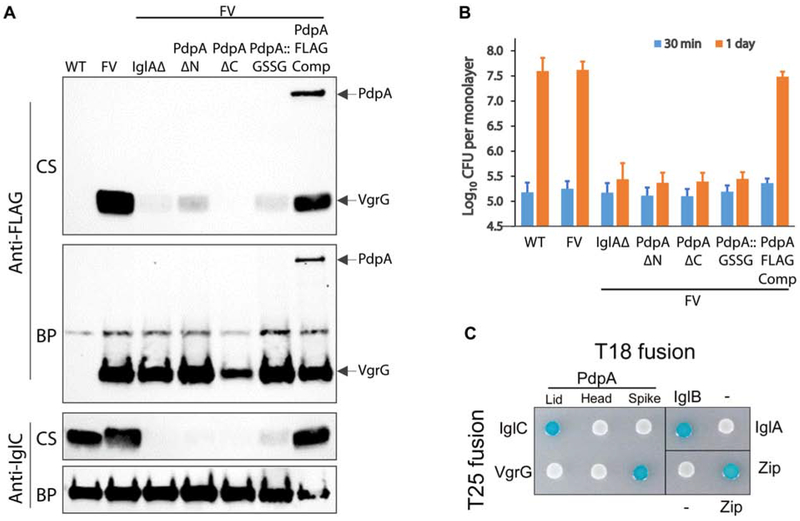
Figure 6. Structure-guided mutagenesis of lid, head, and spike of PdpA.
(A) Secreted products of F. novicida growing in broth with high KCl. Culture supernates (CS) and bacterial pellets (BP) were evaluated by Western immunoblotting. While the F. novicida wildtype (WT) and the strain expressing FLAG-VgrG from the chromosome (FV) secrete IglC and VgrG in response to high KCl, the capability to secrete IglC and VgrG is lost in FV strains lacking IglA (IglAΔ), with N-terminal truncation of PdpA (PdpA ΔN), with C-terminal truncation of PdpA (PdpA ΔC), or with the PdpA GSSG substitution mutation of residues 68 - 75 (PdpA::GSSG). Both VgrG and PdpA are secreted by FV strain in which the truncated PdpA is complemented with a FLAG-tagged PdpA (PdpA FLAG Comp).
(B) Strains defective in Type VI secretion are unable to replicate intracellularly in human THP-1 like macrophages. Strains are designated using the same nomenclature as in (A). Data shown are the means and standard deviations of three independent experiments each with biological triplicates.
(C) Bacterial-two-hybrid analysis shows interaction of the PdpA lid domain with IglC and of the PdpA spike domain with VgrG. Interactions between the head domain and IglC or VgrG were not observed. Positive controls: IglA-IglB and Zip-Zip constructs. Negative controls: IglA-null and Zip-null constructs.
See also Figure S4.