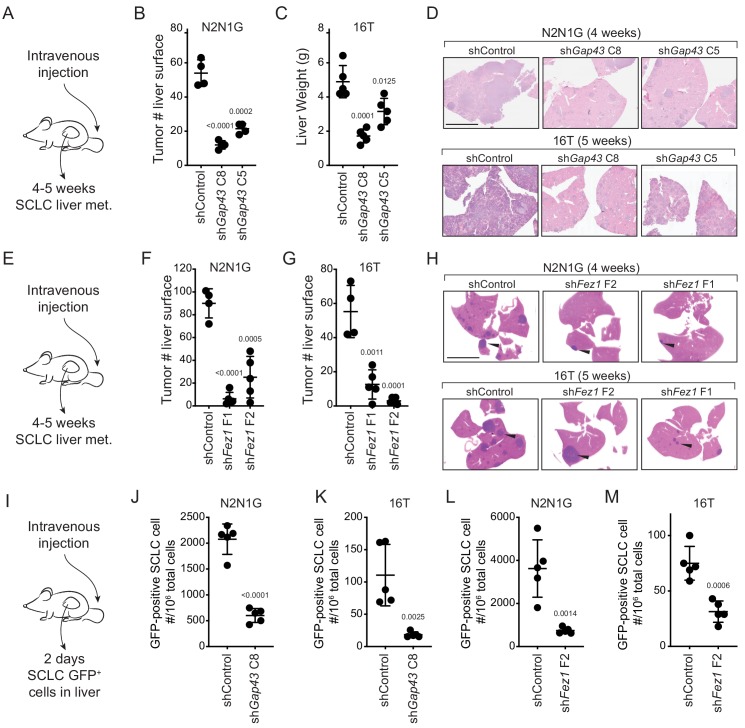
Figure 4. Genes involved in the generation of protrusions also control the formation of metastases.
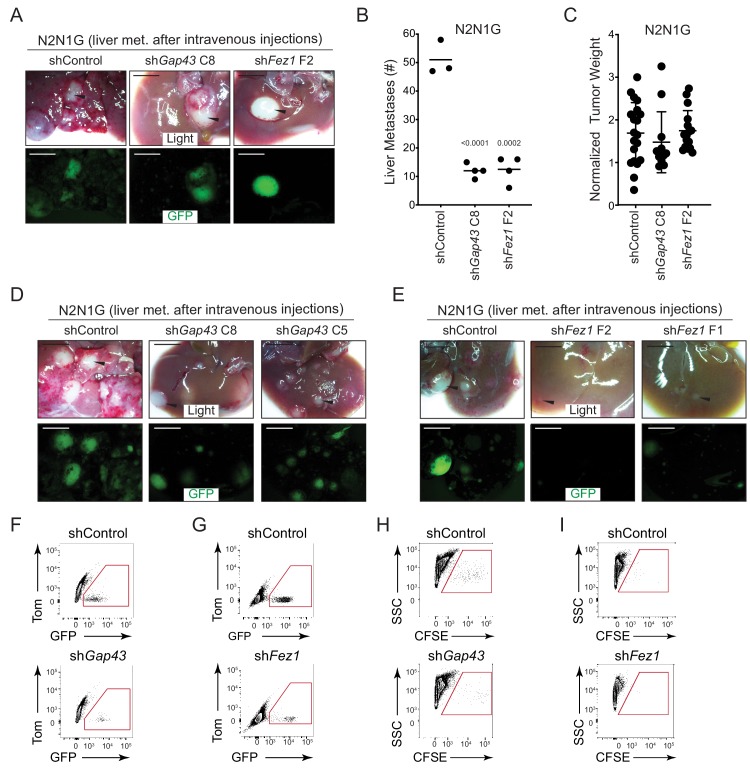
(A) Diagram of the approach to investigate the formation of liver metastases (met.) after intravenous injection of SCLC cells. (B–C) Quantification of the number of metastases 4 and 5 weeks after intravenous injection of N2N1G and 16T mSCLC cells, respectively, with control knock-down or knock-down of Gap43 with two independent shRNAs. For N2N1G, tumors at the surface of the liver were quantified on the liver surface, as shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 2D. Too many tumors were present with the 16 T cell line and the control shRNA, and quantification was thus performed by measuring liver weight. N = 4–5 mice per condition in one biological replicate. Mean + /- s.d. unpaired t-test. (D) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H and E) images of liver sections of mice in (B–C). Scale bars, 5 mm. (E–H) As shown in (A–D) for Fez1 knock-down. See Figure 4—figure supplement 2E for representative images with N2N1G cells for the quantification in (F–G) of tumors at the surface of the liver. Arrows point to metastases. N = 4–5 mice per condition in one biological replicate. Mean + /- s.d. is shown, unpaired t-test. (I) Diagram of the approach to investigate early steps in liver metastasis, 2 days after intravenous injection. (J–M) Quantification of the number of GFPpositiveN2N1G and 16T mSCLC cells 2 days after intravenous injection. See Figure 4—figure supplement 2F-ID for representative flow cytometry. N = 5 mice per condition in one biological replicate. Mean + /- s.d., unpaired t-test.