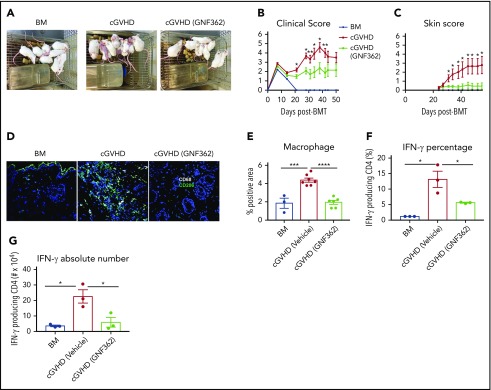
Figure 7.
GNF362 treatment reversed skin disease in mice with cGVHD and scleroderma. Lethally irradiated BALB/c mice underwent B10.D2 BM transplantation, only or with purified B10.D2 T cells (CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells: 1.8 × 106 and 0.9 × 106, respectively). GNF362 treatment was started at day 21. (A) Photographs of mice in the BM only, vehicle-treated, and GNF362-treated cGVHD groups. (B) Clinical manifestations of cGVHD were assessed by scoring weight loss, activity, posture, and fur condition. Healthy mice receive a score of 0. (C) Skin scores were assessed by measuring the area of skin with fur loss or sclerodermatous lesion. Intact skin was given a score of 0 (n = 12 per group). (D) Macrophage CD68, and M2 macrophage CD206 fluorophores were used to stain skin of transplanted mice. Confocal images were acquired on an Olympus FluoView500 Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope at original magnification ×200. (E) Quantification of macrophages (CD68+CD206+) by Fiji software. (F-G) Lymph nodes were harvested and pooled (3 mice lymph nodes for each data point) on posttransplant day 55. Single suspension of lymphocytes from lymph nodes was stimulated in vitro. CD4+ IFN-γ production was evaluated by flow cytometry (n = 3 data points/group). Results shown are representative of 2 independent experiments with similar results. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, and ****P < .0001.