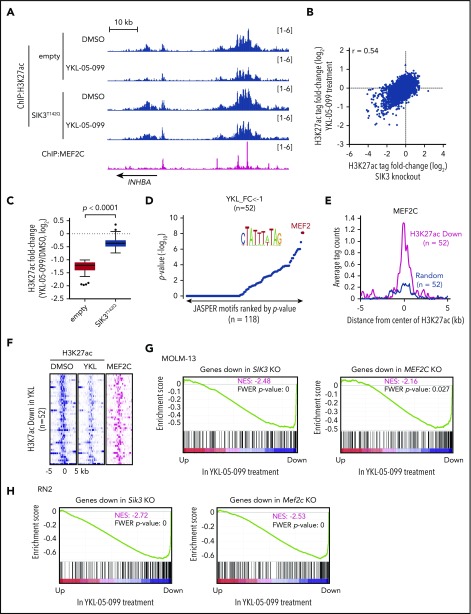
Figure 3.
YKL-05-099 interferes with MEF2C-dependent transcriptional activation. (A) ChIP-seq profiles of H3K27ac and MEF2C at the indicated genomic loci, chosen because H3K27ac is decreased in MOLM-13 cells by YKL-05-099 treatment. For H3K27ac ChIP-seq, cells were harvested after 2-hour treatment with DMSO (0.1%) or 250 nM YKL-05-099. (B) Scatterplot of H3K27ac fold-change after SIK3 knockout or YKL-05-099 treatment at 16 437 genomic sites of H3K27ac enrichment. (C) Box plots of fold change of downregulated H3K27ac signals in MOLM-13 cells treated with DMSO or 250 nM YKL-05-099 for 2 hours. MOLM-13 cells express either an empty vector or SIK3T142Q cDNA. (D) TRAP motif enrichment analysis of DNA sequences with decreased H3K27ac after YKL-05-099 treatment. (E) A meta profile of MEF2C occupancy at the genomic regions exhibiting H3K27ac log2-fold change of <−1 after YKL-05-099 treatment vs a randomly chosen set of H3K27ac-enriched sites. (F) ChIP-seq density plot at regions with decreased H3K27ac after YKL-05-099 treatment. Enhancers are ranked by fold change of H3K27ac after treatment. (G) GSEA, which evaluates how treating MOLM-13 cells with YKL-05-099 (250 nM, 2 hours) influences previously defined gene signatures that were suppressed after SIK3 or MEF2C knockout in this cell type.22 Normalized enrichment score (NES) and family-wise error rate (FWER) P value are shown. (H) GSEA that evaluates how treating RN2 cells with YKL-05-099 (250 nM, 2 hours) influences gene signatures that are suppressed after Sik3 or Mef2c knockout in this cell type. NES and FWER P value are shown.