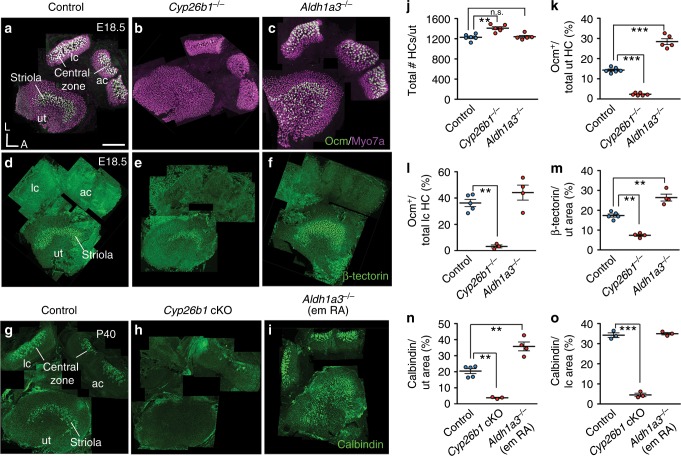
Fig. 2. Disruption of RA signaling alters striolar/central zone formation.
a Oncomodulin (Ocm) is expressed in type I HCs in striolar/central zones, whereas all HCs are positive for Myosin7a of controls. b, c, j Total HC number is increased in Cyp26b1−/− (1394 ± 39, P = 0.014, n = 6), but unchanged in Aldh1a3−/− utricles (1285 ± 28, P = 0.419, n = 5), compared to controls (1229 ± 30, n = 6). b, c, k Percentages of Ocm+ HCs (14.3 ± 0.5 in controls, n = 6) are decreased in Cyp26b1−/− (2.3 ± 0.2, n = 6, p < 0.0001) and increased in Aldh1a3−/− utricles (28.4 ± 1.4, n = 5, P < 0.0001). b, c, l Percentages of Ocm+ HCs in lateral cristae (lc, 36.2 ± 2.7 in controls, n = 5) are reduced in Cyp26b1−/− (3.2 ± 1.1, n = 3, P = 0.0005), but unchanged in Aldh1a3−/− mutants (44.1 ± 5.6, n = 4, P = 0.302). d Anti-β-tectorin labels SCs in striolas of utricles. e, f, m β-tectorin+ domain, as % of total utricular macular area (17.4 ± 0.9 in controls, n = 5), is reduced in Cyp26b1−/− (7.4 ± 0.6, n = 4, P = 0.0002) and increased in Aldh1a3−/− (26.4 ± 1.7, n = 4, P = 0.0003) utricles. g Anti-calbindin labels calyceal nerve endings in striolar/central zones. h, i, n, o Expression and percentage of calbindin-positive area is reduced in utricles (3.8 ± 0.3, n = 3, P = 0.0005) and cristae (4.7 ± 1.4, n = 3, P < 0.0001) of Cyp26b1 cKO, but increased in utricles (36.0 ± 6.6, n = 4, P = 0.0006) and unchanged in cristae (34.4 ± 0.5, n = 3, P = 0.3021) of Aldh1a3−/− (em RA) mutants, compared to respective controls (n, 19.7 ± 1.7, n = 5; o, 34.2 ± 1.1, n = 3). Error bars: SEM. Significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA for all panels. A, anterior; L, lateral. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. n.s., not significant. Scale bar: 200 μm.