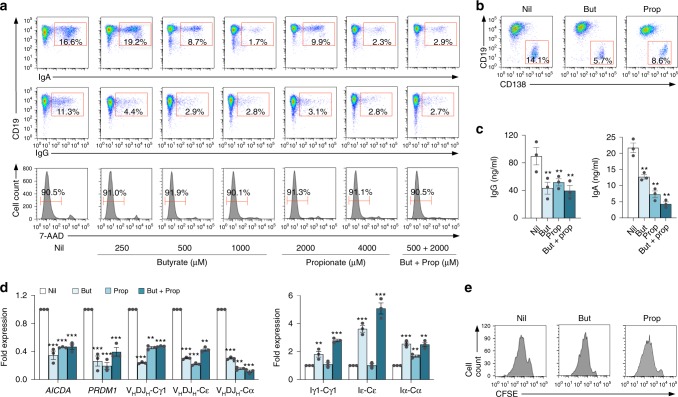
Fig. 6. Butyrate and propionate inhibit AICDA and PRDM1 expression, and reduce CSR and plasma cell differentiation in human B cells.
a Human B cells purified from PBMCs of healthy subjects were stimulated with CD154 plus IL-4 and IL-21, in the presence of nil, butyrate (250, 500, or 1000 μM), propionate (2000 or 4000 μM), or butyrate (500 μM) plus propionate (2000 μM). The proportions of CD19+ IgA+ and CD19+ IgG+ as well as viable (7-AAD–) CD19+ B cells were analyzed 120 h post stimulation by flow cytometry. Data are representative of three independent experiments yielding comparable results. b–d Human B cells were stimulated with CD154 plus IL-4 and IL-21, in the presence of nil, butyrate (500 μM), propionate (2000 μM), or butyrate (500 μM) plus propionate (2000 μM). CD19loCD138+ plasma cells were analyzed 120 h post stimulation by flow cytometry (b). IgG and IgA titers in culture fluids of these B cells were analyzed 120 h post stimulation by ELISA. Data are from three independent experiments (mean and SE) (c). Expression of AICDA and PRDM1, germline Iγ1-Cγ1, Iα-Cα, and Iε-Cε, as well as mature VHDJH-Cγ1, VHDJH-Cε, and VHDJH-Cα transcripts were analyzed 72 h post stimulation by qRT-PCR and normalized to the expression of HRPT. Data are ratios to stimulated B cells cultured with nil (set as 1; means ± SEM of three independent experiments) (d). e Human B cells were labeled with CFSE and stimulated with CD154 plus IL-4 and IL-21 in the presence of nil, butyrate (500 μM), or propionate (2000 μM) for 96 h. CFSE intensity were analyzed by flow cytometry. Progressive left shift of fluorescence intensity indicates CD19+ B-cell division. Data are representative of three independent experiments yielding comparable results. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (unpaired t test). The source data are provided in Source Data file.