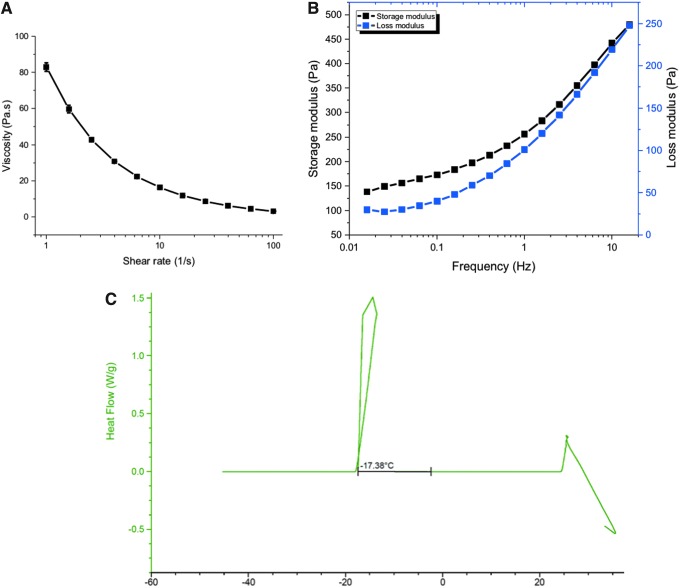
Figure 3.
(A) On a stress-controlled rheometer, homogenized hydrogels were analyzed via shear rate sweeps to calculate the viscosity, as an indication of injectability into the PWDs. The geometry used were rough-surfaced 1 degree 40 mm Cone-and-Plate at a gap of 400 μm. (B) The storage modulus is larger than the loss modulus; it is indicative that we have a gel and not a viscous liquid. Also, the moduli are quite low, demonstrating that we have a very soft hydrogel. A strain sweep is used to determine the linear viscoelastic area of the hydrogel, and a frequency sweep is used to determine the linear equilibrium modulus plateau of the hydrogel. (C) DSC measurements of the hydrogel sample from room temperature to −45°C at a rate of 0.1°C per minute. The freezing point is indicated by a positive heat flow into the hydrogel sample during the cooling cycle beginning at −17.38°C. DSC, differential scanning calorimetry.