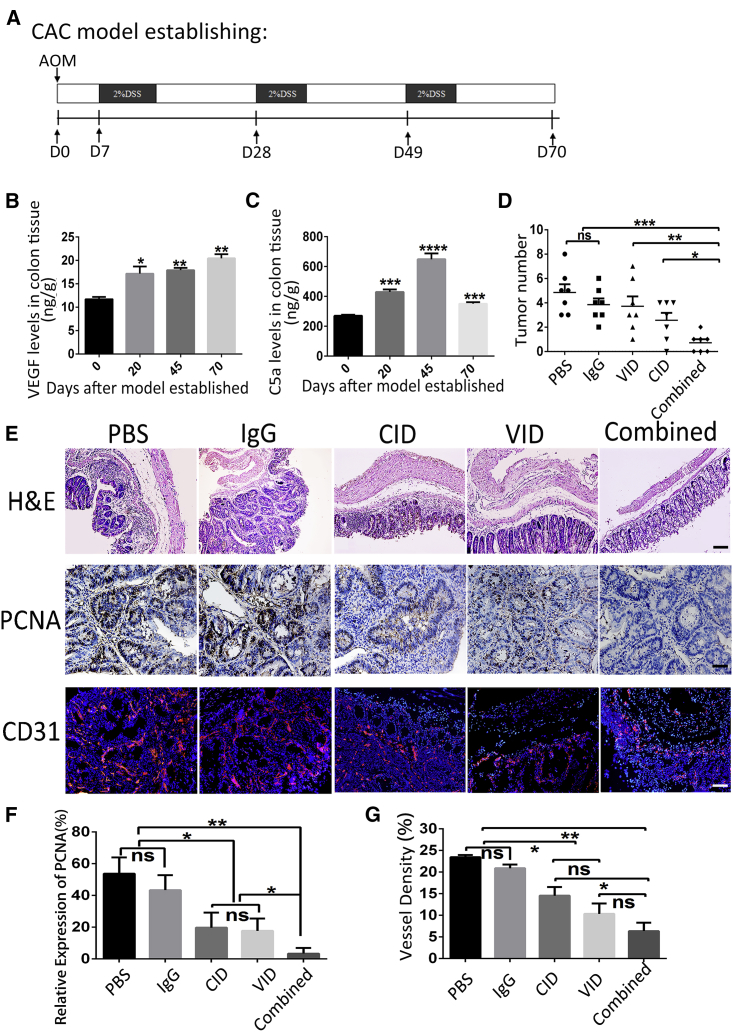
Figure 4.
Combination of VID and CID Reduces CAC Tumorigenesis
(A) Schematic overview of CAC regimen. (B and C) At the indicated time points after initiation of CAC induction, colons were homogenized, and supernatants were prepared for the detection of VEGF (B) and C5a (C) protein levels. Each group consisted of 3–4 mice. The error bars represent SD (***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; *versus day 0, all groups are compared to D0 ). (D) Number of tumors in colon and rectum was counted, with bars representing SD. ns, not significant. (E) H&E, PCNA, and CD31 staining of the colon of mice. For H&E staining: original magnifications, 100×. Scale bars, 100 μm. (F) Representative immunohistochemistry images with antibody to PCNA in different groups; original magnifications, 200×; and quantification analyses of PCNA-positive cell number, with error bars representing SD (*p < 0.01; **p < 0.005; ns, not significant). (G) Immunofluorescence analysis using anti-CD31 (red) antibody indicates the blood vessel outlines of different groups. The error bars represent SD (*p < 0.01; **p < 0.005; ns, not significant). 100×; scale bar, 100 μm.