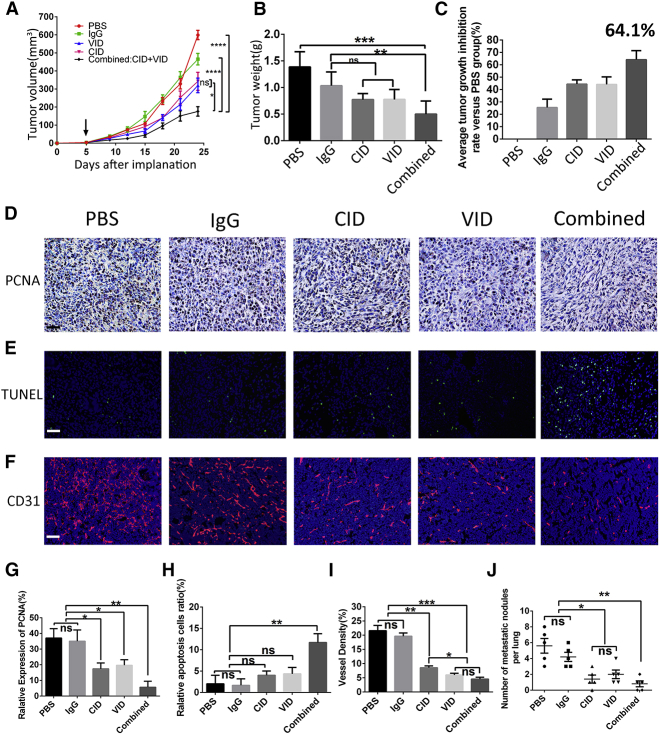
Figure 6.
Combination of VID and CID Suppresses Tumor Growth in Breast-Tumor-Bearing Mice
(A) Comparison of tumor growth; arrow indicates the start of injections. Error bars represent SD (*p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant). (B) Tumor weight of mice in each group was measured on the days indicated, with error bars representing SD. (C) Results of tumor inhibition rate in each experimental group. (D–I) In (D) and (G), representative immunohistochemistry images (D) are shown with antibody to PCNA in different groups (original magnifications, 200×; scale bar, 50 μm) and quantification analyses (G) of PCNA positive-cell number are presented, with error bars representing SD (*p < 0.01; **p < 0.005; ns, not significant). (E and H) Detection of apoptosis of tumor cells by TUNEL (E) (200×; scale bar, 50 μm) and quantification analyses of TUNEL-positive cell numbers (H), with error bars representing SD (**p < 0.005; ns, not significant). (F and I) Immunofluorescence analysis (F) using anti-CD31 (red) antibody shows blood vessel outlines of different groups; in quantification analyses (I), error bars represent SD (*p < 0.01; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.005; ns, not significant; 100×; scale bar, 100 μm). (J) Quantification of lung metastasis nodule of 4T1 cells in different groups, with error bars representing SD (*p < 0.01; **p < 0.005; ns, not significant).