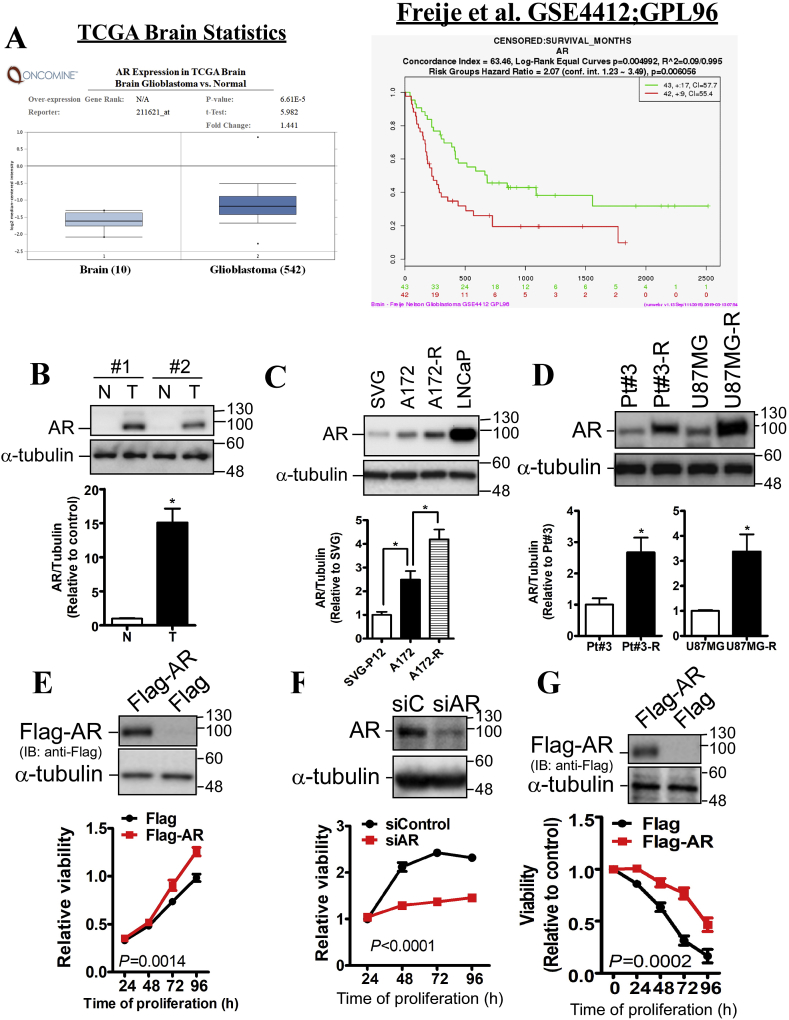
Fig. 1.
The correlation of AR expression with prognosis and drug resistance in glioblastoma. A. Bioinformatics analysis for AR in glioblastoma. The mRNA expression of AR in normal brain and glioblastoma tissues was compared in the TCGA dataset using the Oncomine website. The correlation of AR mRNA expression with prognosis was acquired from GSE4412 released by Freije et al. using the SurvExpress website. P-value was indicated. B. The protein level of AR in human specimens was analyzed using western blotting. N: normal brain tissue; T: glioblastoma tissue. The results of two paired specimens were quantitated. Data were expressed as mean ± s.e.m. (*p < 0.05). C, D. The expression of AR in multiple cell glioblastoma cell lines and a prostate cancer cell line, LNCaP (positive control). SVG p12 (SVG) is an immortalized fetal glial cell line. Experiments were performed three times independently, and data were expressed as mean ± s.e.m. (*p < 0.05). E. After transfection with Flag-AR or siRNA-mediated AR knockdown (F) for 2 days, U87MG-R cells viability was estimated by MTT assay. G. After transfection with Flag-AR for 24 h, U87MG cells were treated with 100 μM TMZ for the indicated interval. Viability was estimated by MTT assay. Experiments were performed three times independently, and data were expressed as mean ± s.e.m. The significant difference between control and knockdown/overexpression groups was analyzed using two-way ANOVA. P-value was indicated. The cell lysates were subjected to western blotting to confirm Flag-AR expression and AR knockdown.