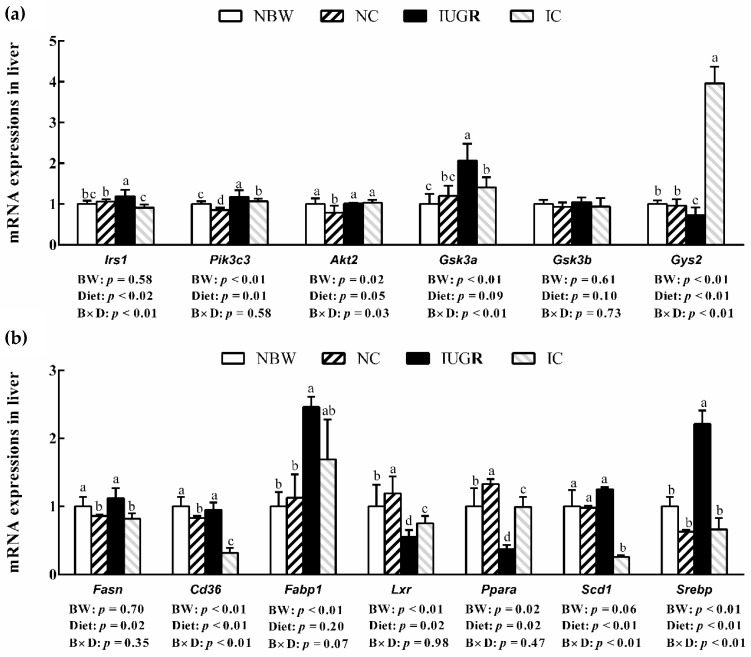
Figure 3.
Influence of curcumin on the hepatic mRNA expressions of IUGR weaned piglets (a) insulin signal pathway, (b) lipid metabolism; 50 d). Values are the means ± standard deviation; n = 8/group. abcd denotes significant differences (p < 0.05). NBW, piglets with normal birth weights and fed with control diets; NC, NBW piglets fed with curcumin diets; IUGR, piglets with intrauterine growth retardation and fed with control diets; IC, IUGR piglets fed with curcumin diets; B, birth weight of piglets; D, curcumin diets; B × D, the interaction between the birth weight and curcumin diets. Irs1, insulin receptor substrate 1; Pik3c3, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3; Akt2, serine/threonine kinase 2; Gsk3a, glycogen synthase kinase 3 alpha; Gsk3b, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; Gys2, glycogen synthase 2; Fasn, fatty acid synthase; Cd36, cluster of differentiation 36; Fabp1, liver fatty acid binding protein 1; Lxrα, liver × receptor; Ppara, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; Scd1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase1; Srebp, sterol regulatory element binding proteins.