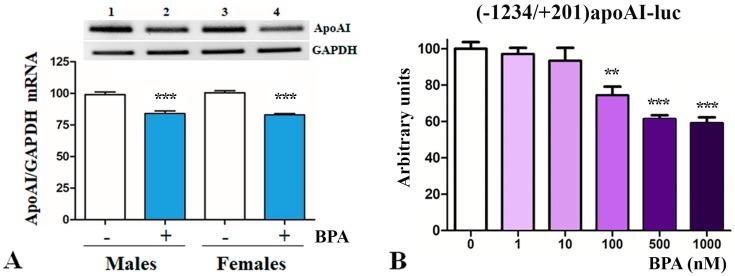
Figure 3.
Down-regulatory effect of BPA on apoA-I in hepatocytes. (A) Real-Time PCR data showed that BPA treatment of LDLR−/− mice significantly decreased hepatic apoA-I mRNA levels as compared to control mice, as depicted in the graph. Representative images illustrate the expression of apoA-I and GAPDH genes in the liver, as detected by RT-PCR. (B) Transiently transfected HepG2 cells with [−1234/+201]apoAI-luc construct were treated with BPA (1–1000 nM) and the activity of apoA-I promoter was assessed by luciferase assays. BPA treatment with low concentrations (1 and 10 nM) had no effect on apoA-I promoter activity, while higher concentrations (100–1000 nM) decreased the activity of apoA-I promoter. Statistical significance ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005.