Figure 3.
The Human Nigro-striatal Pathway Establishes a Stable Synaptic Connectivity
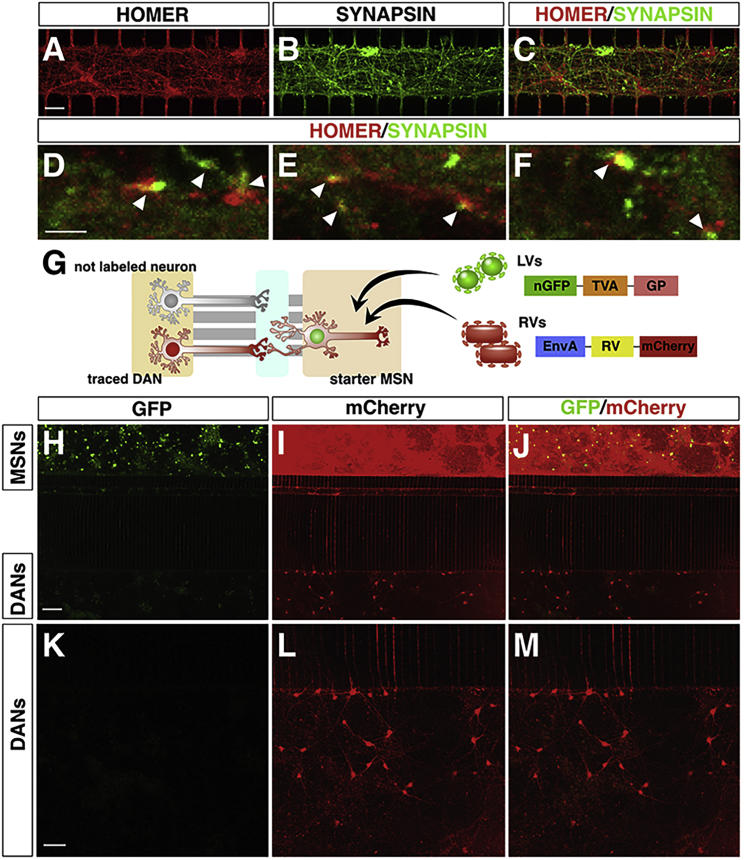
(A–F) Representative pictures of single and double staining for Synapsin and Homer to visualize pre- and post-synaptic terminals, respectively (arrowheads in D, E, and F).
(G) Illustration of the lentiviral and rabies viral vectors used in this experiment. The tracing vector transduces the cells with a nuclear GFP, the TVA receptor, and G replication factor necessary for rabies infection. Neurons infected with the tracing virus are termed starter MSNs. After rabies viral infection, these cells express mCherry, and because of the presence of GP, the rabies viruses spread retrogradely to the traced neurons.
(H–M) Representative images of connectivity between MSNs and DANs. Starter MSNs are positive for both GFP and mCherry (H–J) indicating rabies viral productive infectivity.
(K–M) DANs express mCherry, but not GFP, indicating active spreading of the rabies viruses from MSNs and DANs and stable connectivity between the two neuronal networks.
Scale bars, 100 μm.