Figure 1.
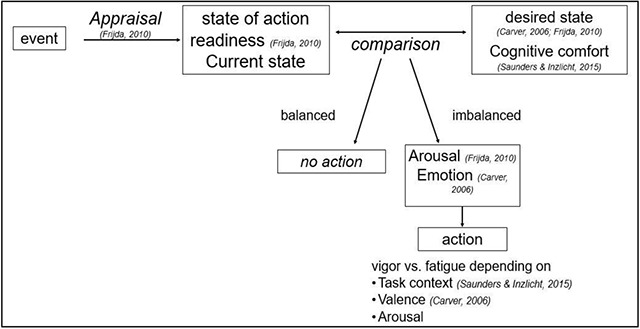
Summary of the main theoretical accounts of impulsive action. All theories assume that the comparison between the current state and the desired state (e.g. cognitive comfort) leads to actions. However, the theories assume different reasons for an action being invigorated or not.
