Figure 1.
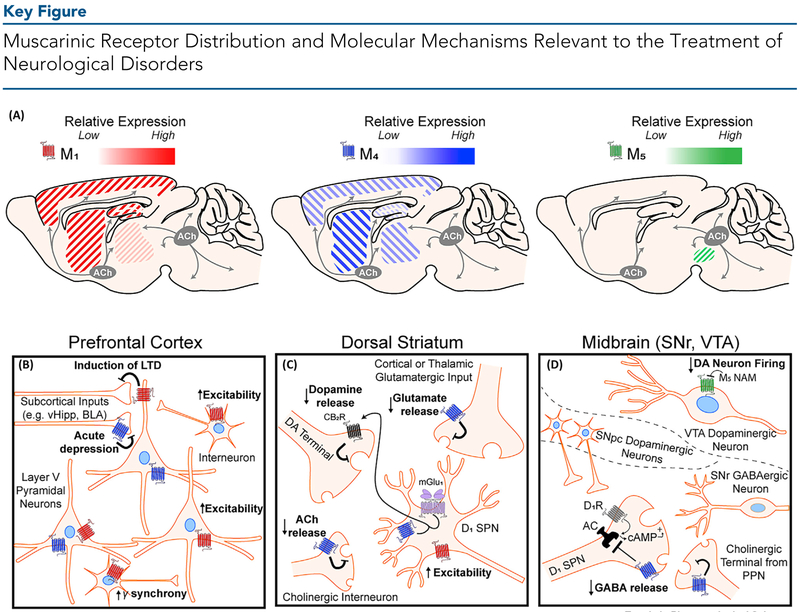
(A) Distribution of M1, M4, and M5 muscarinic acetylcholine (ACh) receptors in brain regions implicated in neurological dysfunction. The relative expression of each receptor subtype is indicated by its respective color gradient. M2 and M3 (not shown) muscarinic ACh receptors (mAChRs) are also expressed widely throughout the brain. M1 mAChRs are highly expressed in the cortex, hippocampus, and dorsal and ventral striatum, and are expressed at low levels in thalamic areas. M4 mAChRs are highly expressed in striatal regions, moderately expressed across the cortex and thalamus, and are poorly expressed in the hippocampus. M5 mAChR expression is restricted to the midbrain. Cholinergic projection neurons produce and release ACh from two distinct clusters – the basal forebrain nuclei (grey circle, left) which innervates cortical, hippocampal, and thalamic areas, and the brain stem nuclei (grey circle, right) which innervates midbrain, hindbrain, thalamic, and cerebellar areas. Cholinergic tone in the dorsal and ventral striatum is primarily provided by large cholinergic interneurons (not depicted). (B) In the prefrontal cortex, M1 mAChR activation induces a form of long-term depression (LTD) of glutamatergic inputs from subcortical areas including the ventral hippocampus (vHipp) and basolateral amygdala (BLA). M1 mAChR activation also increases the excitability of pyramidal neurons and GABAergic interneurons. Activation of M1 via interneurons can also increase gamma oscillation synchrony in the cortex. M4 mAChRs can acutely inhibit neurotransmitter release. (C) In the dorsal striatum, M4 mAChRs expressed on direct pathway D1 receptor-positive spiny projection neurons (SPNs) interact with metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGlu1) to produce endocannabinoids which then bind to cannabinoid type 2 (CB2) receptors to inhibit local dopamine release. In addition, M4 activation can reduce both ACh release from local cholinergic interneurons and act as a heteroreceptor on glutamatergic terminals from the cortex and thalamus to reduce glutamate release. M1 mAChRs expressed on D1-SPNs increase the excitability of these neurons. (D) In the midbrain, cholinergic modulation of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and direct pathway input into the substantia nigra reticulata (SNr) are relevant to neurological disorders. In the VTA (top), M5 mAChRs are expressed on VTA DA neurons and M5 negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) are hypothesized to reduce DA neuron firing. In the SNr (bottom), M4 mAChR activation on direct pathway D1-SPN terminals directly opposes increased GABA release mediated through D1-receptor activation by DA released from the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc, middle). M4 can also act as an autoreceptor and reduce ACh release from cholinergic projection terminals.