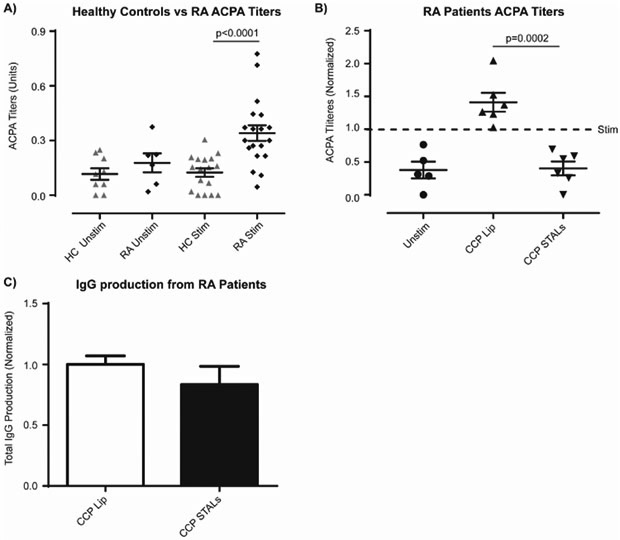
Figure 4.
CCP STALs prevent ACPA production from rheumatoid arthritis patients in vitro. a) Human B-cells were isolated from healthy control (N=4 each an independent experiment, pooled data, one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons) or rheumatoid arthritis (N=4 each an independent experiment, pooled data, one-way ANOVA with multiple comparison) patients’ PBMCs. RA patients were pre-screened for high titers of ACPA. B-cells were plated and either left unstimulated (PBS), or stimulated under standard stimulating conditions for 7 days, and ACPA titers in individual wells are shown. b) B-cells were isolated from RA patient PBMCs and left unstimulated or stimulated in accordance with the above conditions with CCP decorated-liposomes (CCP Lip) or CCP+hCD22L decorated liposomes (CCP STALs) for the entirety of the study. Supernatants from the wells were assessed for ACPA titers and normalized titers of individual patient are shown (N=6 each an independent experiment with an individual RA patient sample, unstim. N=5 (one patient did not have enough B-cells for all conditions), Stim. N=6, CCP Lip N=6, CCP STALs N=6, pooled data, one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons). c) Total IgG titers in supernatants was measured (N=4 for CCP Lip and CCP STALs, each an independent experiment with an individual RA patient sample, pooled data, one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons).