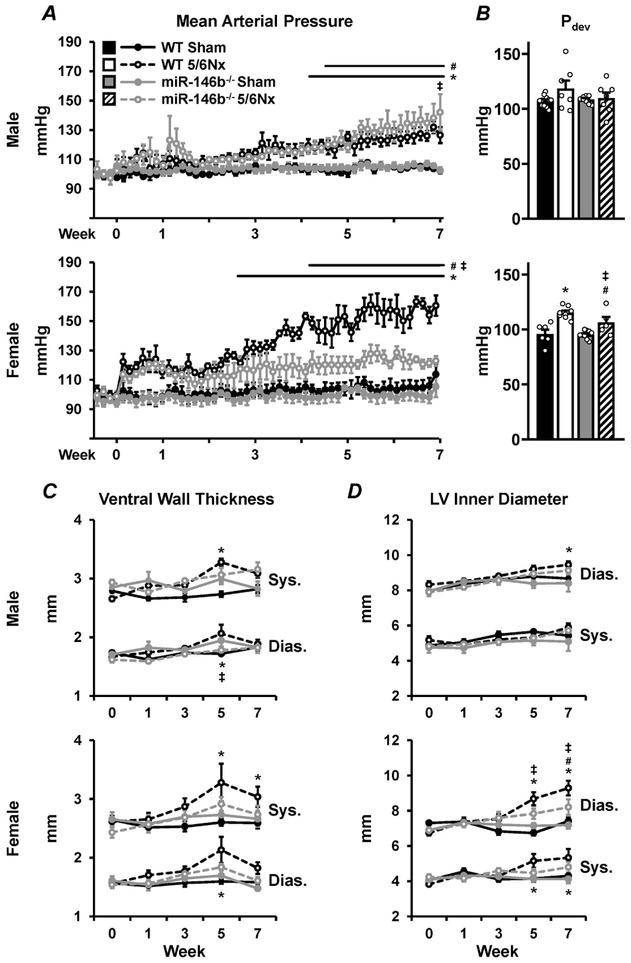
Figure 5: Chronic blood pressure monitoring reveals sex-specific divergence of cardiovascular pathologies.
Chronic radiotelemetry implants used to measure (A) conscious ambulatory blood pressure in males (top) and females (bottom), here reported as MAP. (B) LV developed pressure was measured acutely at week 7 with the use of a Millar pressure catheter. LV structure was measured using echocardiography to monitor (C) ventral wall thickness and (D) LV chamber diameter throughout the cardiac cycle. All data presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3-15/group; * p<0.05 WT 5/6Nx vs. WT Sham; # p<0.05 miR-146b−/− 5/6Nx vs. miR-146b−/− Sham; ‡ p<0.05 miR-146b−/− 5/6Nx vs. WT 5/6Nx; & p<0.05 miR-146b−/− 5/6Nx vs. WT 5/6Nx.