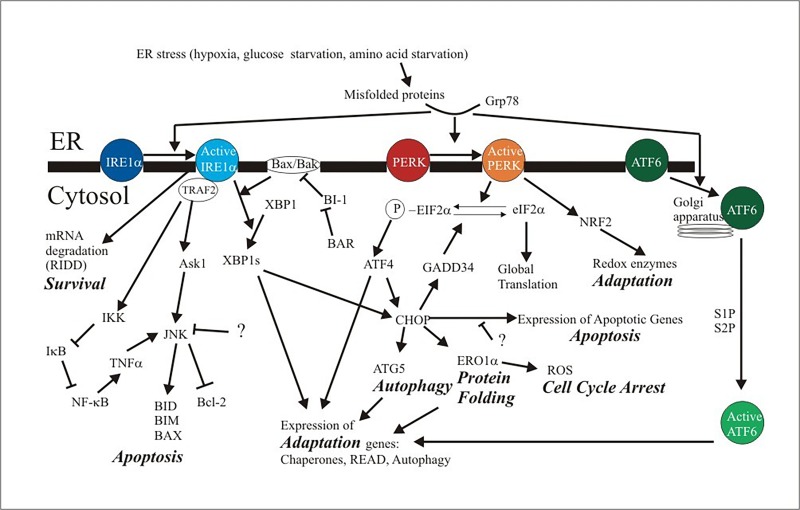
Figure 1. UPR signaling.
ER stress triggers dissociation of IRE1α, PERK and ATF6 from GRP78, activating the 3 ER stress sensors. IRE1α activates transcription factor XBP1, leading to the expression of a series of target genes that aim to restore the homeostasis of ER. Additionally, IRE1α performs RIDD to promote cell survival, and under certain situations, it might also promote apoptosis via the TRAF2/ASK1/JNK pathway and the CHOP pathway. Activated PERK disables eIF2α and suppresses global protein synthesis, and selectively promotes ATF4 to upregulate the expression of genes involved in redox, amino acid metabolism, and protein folding. ATF4 may also upregulate CHOP to induce apoptosis. Furthermore, CHOP induces expression of ERO1α to promote disulfide bond formation while generating ROS; CHOP also upregulates GADD34 to dephosphorylate eIF2α, as a feedback control to recover protein synthesis. Stress-induced ATF6 translocates to the Golgi to be processed and becomes an active transcription factor and mainly induces cytoprotective responses. The molecular mechanisms to control apoptosis while promoting cell survival have not been identified.