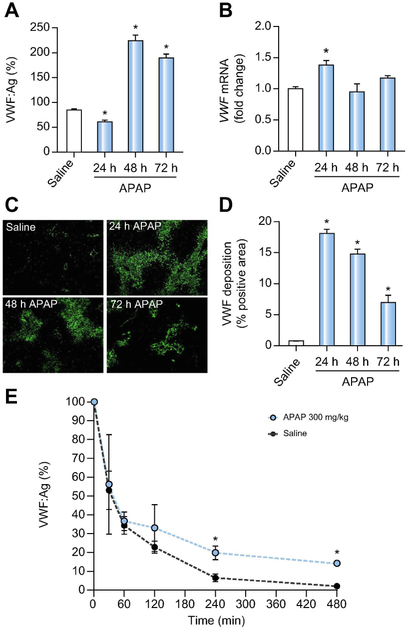
Figure 1. Impact of APAP-induced acute liver injury on plasma and hepatic VWF.
Male wild-type mice were given 300mg/kg APAP or saline (i.p.) and samples were collected 24h, 48h, and 72h later. (A) VWF plasma antigen (VWF:Ag) levels were determined by ELISA.. Levels are expressed as % of normal pooled mouse plasma which was set at 100%. (B) Hepatic mRNA levels of VWF in wild-type-challenged mice. (C) Representative images of hepatic VWF immunofluorescent labeling (green) (D) Quantification of hepatic VWF deposition, expressed as percentage of positive pixel count. For E, male VWF−/− mice were challenged with saline (black dashed line) or 300mg/kg APAP (i.p.) (red line) and 24h after challenge, the mice were given 3U of Humate-P® by intravenous injection. Human VWF:Ag levels were determined by ELISA various times after VWF administration, and expressed as % of infused VWF amount set to 100%. Bars represent mean ± standard error of mean (n = 5-12 mice per group for panel A-D, n=3-6 mice per time point for panel E) *p <0.05 compared to saline-treated animals.