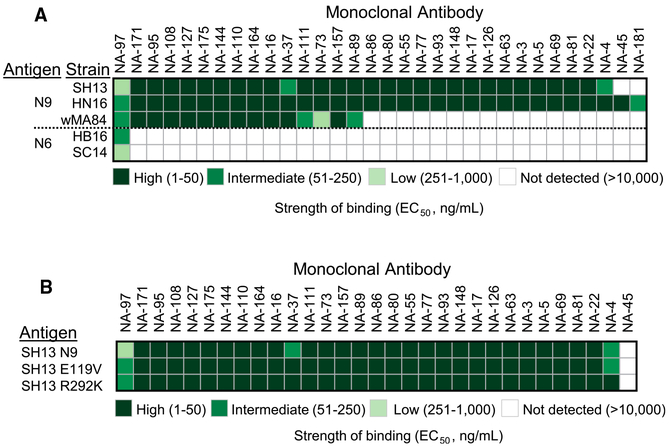
Figure 2. Binding of N9-Reactive mAbs Is Subtype-Specific and Is not Affected by Mutations Causing Resistance to Neuraminidase Inhibitors.
(A) A panel of 35 human mAbs was isolated on the basis of reactivity to recombinant SH13 N9 NA antigen. Cross-reactivity of N9-reactive mAbs to recombinant NA proteins from group 1 was measured by ELISA. Representative EC50 values (ng/mL) from two independent experiments are plotted as a heatmap. NAs were clustered by amino acid sequence phylogeny. Three mAbs that bind N9 antigen with EC50 value higher than 10 μg/mL (highest tested concentration) excluded from representation.
(B) Binding of N9-reactive mAbs to recombinant wild-type N9 NA from A/Shanghai/2/2013 virus or NI-resistant mutants was measured by ELISA. Representative EC50 values (ng/mL) from two independent experiments are plotted as a heatmap. Four mAbs that bind N9 SH13 antigen with EC50 value higher than 10 μg/mL (highest tested concentration) excluded from representation.