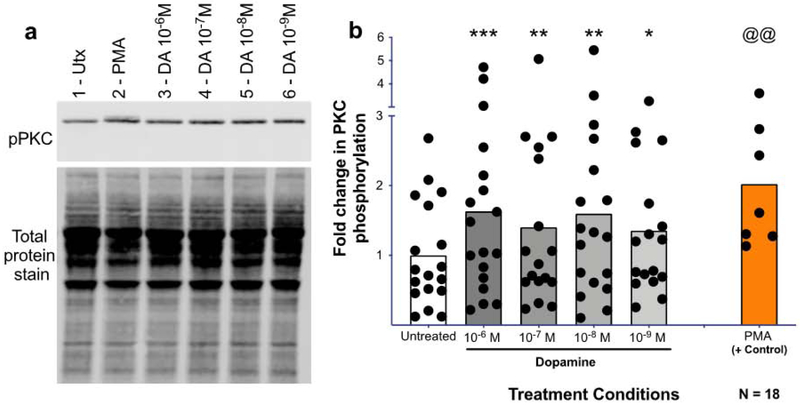
Figure 6 -. Dopamine induces PKC phosphorylation in human macrophages.
Human MDMs were treated with dopamine for 1 minute and protein was isolated, run on a western blot, and probed for phospho-PKC (bII Ser660). A representative western blot is shown in (A, 1-Untx, 2-PMA 10−6 M, 3-DA 10−6 M, 4-DA 10−7 M, 5-DA 10−8 M, 6-DA 10−9 M)). Dopamine significantly increased PKC phosphorylation at 10−6M, 10−7M, 10−8M, and 10−8M after 1 minute relative to the untreated control (B, DA, gray column, Utx, white column). Phospho-PKC signal was normalized to total protein for all donors, and analyzed using a one-way ANOVA. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005. PMA (orange) was used as a positive control and was analyzed separately using a Paired T-test. @@ p<0.01. Data is expressed as fold change compared to the mean of the untreated.