Figure 1:
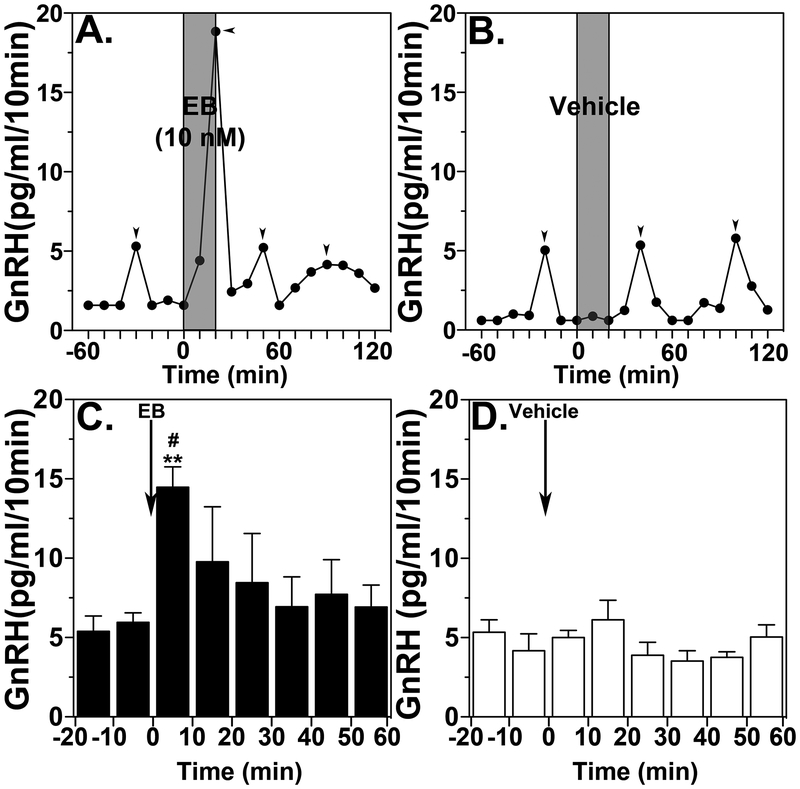
Brief direct infusion of EB into the median eminence induces GnRH release. Representative case and group data (means ± SEM) from EB infusion (A and C) or vehicle infusion (B and D) are shown. Time zero designates the beginning of a 20-min EB or vehicle infusion (indicated by grey bars). Two-way ANOVA, indicates that EB significantly stimulated GnRH release (C) over vehicle control (D, p=0.0018). Post-hoc analysis indicates that GnRH levels during the first 10-min of EB infusion were higher than those during the control period (C, **: p<0.01) as well as the corresponding time period of vehicle infusion (D, #: p<0.05). Arrowheads indicate pulses identified by PULSAR. From Kenealy et al., 2013. Permission pending.