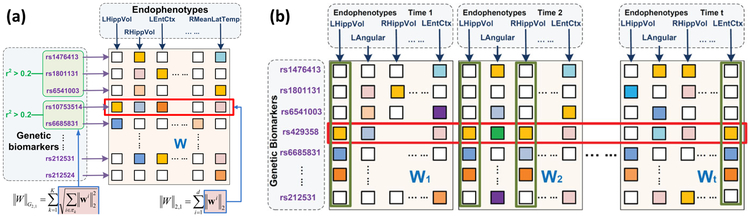
Fig. 7.
Example structured sparse multivariate multiple regression models, where only regression weight matrices W are shown here. Let X be genotype data and Y be imaging QT data. (a) Illustration of the G-SMuRFS model [148] (), where the group l2,1-norm regularization (∥W∥G2,1) does feature selection at the group level (e.g., LD-block), and the l2,1-norm regulesization (∥W∥2,1) does feature selection at the individual SNP level. [Image is reproduced here with permission from Oxford University Press [148]]. (b) Illustration of the TSAL model [149] (), where is a Schatten p-norm regularization term to identify low rank structures (e.g., four green boxes sharing similar patterns), and is an l2,1-norm to select SNPs correlated to most QTs over time (e.g., the red box). [Image is reproduced here with permission from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. [149]].