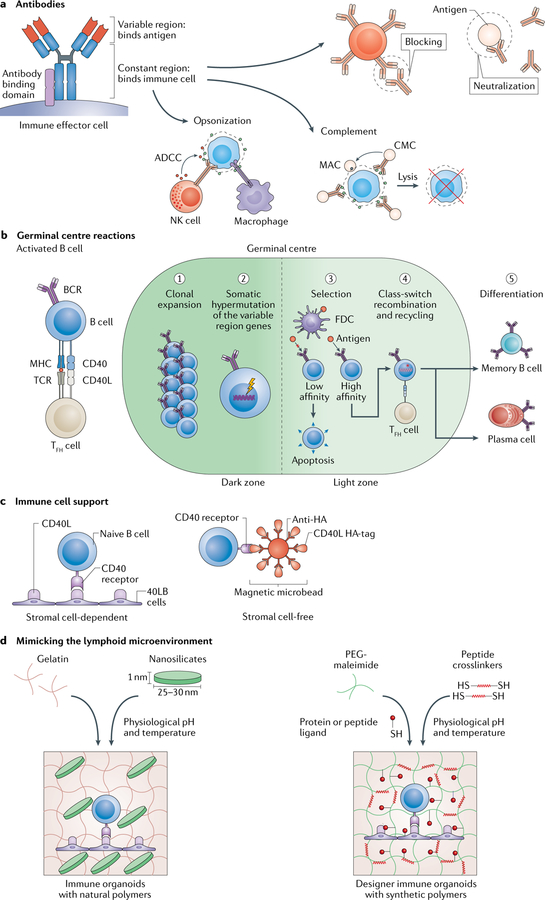
Fig. 5 |. Engineering the germinal centre.
a | Antibodies contain a variable region that binds antigens and a constant region that binds immune cells, which leads to specific cell responses: neutralization, receptor blocking, opsonization, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement activation. ADCC can be carried by out several immune effector cells, including natural killer (NK) cells. Complement activation can either mark an antigen for opsonization or lead to complement-mediated cytotoxicity (CMC), which causes cell lysis through the formation of a membrane attack complex (MAC), b | In the germinal centre, antigen-specific plasma cells, memory B cells and antibodies are produced. B cells are activated once an antigen crosslinks a B cell receptor (BCR), which leads to antigen processing and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presentation. Moreover, the centre becomes compartmentalized into two zones (dark and light zones). After receiving co-stimulatory signals, such as CD40 ligand (CD40L) from T follicular helper (TFH) cells, which binds to the CD40 receptor on the B cell surface, B cells in the dark zone undergo clonal expansion followed by somatic hypermutation of the antigen-binding antibody variable region. In the light zone, B cells presenting high-affinity BCRs for the antigen are selected to survive and undergo class-switch recombination of the antibody constant region to define the downstream immune response. The germinal centre reaction is completed by terminal differentiation of B cells into antigen-specific antibody-secreting cells, such as plasma cells or memory B cells, c | 2D approaches can be applied for immune cell support. Engineered stromal cells (40LB cells) or iron oxide magnetic microbeads presenting both CD40L and antigen can be used to bind naive B cells, d | The lymphoid microenvironment can be modelled using 3D hydrogels to recreate the events during high-affinity antibody generation. Gelatin can be reinforced using 2D nanosilicates to form a hydrogel for the creation of germinal centre organoids ex vivo. Alternatively, a polyethylene glycol (PEG)-maleimide hydrogel can be functionalized with protein or peptide ligands to trigger an antigen-specific immune response. FDC, follicular dendritic cell; TCR, T cell receptor.