Figure 3.
PRMT5 Regulates NHEJ, HR, and G2 Arrest in Response to IR
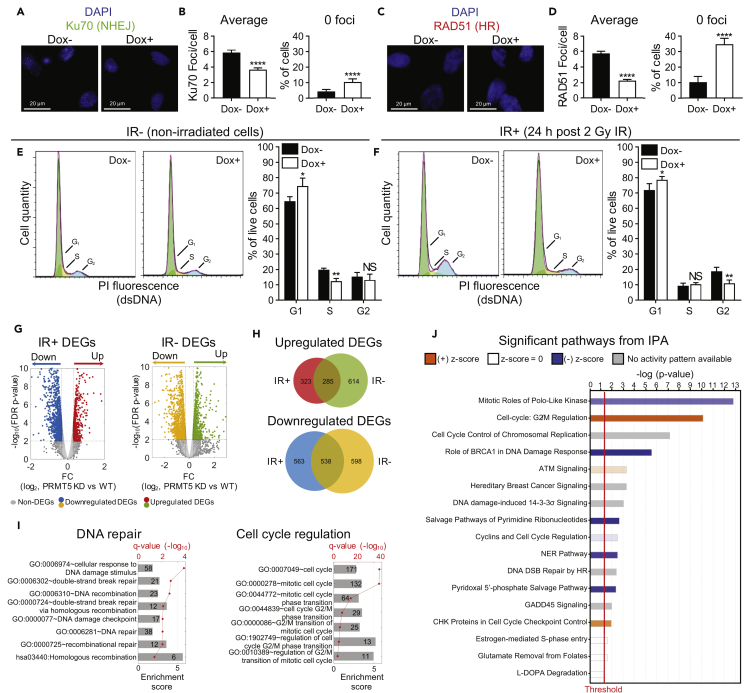
(A) NHEJ repair foci (Ku70) 1 h post 2 Gy IR in LNCaP-shPRMT5 cells with (Dox+) and without (Dox−) PRMT5 knockdown.
(B) Quantification of Ku70 foci from A as described in Figure 2B.
(C) HR repair foci (RAD51) 1 h post 2 Gy IR in LNCaP-shPRMT5 cells with (Dox+) and without (Dox−) PRMT5 knockdown.
(D) Quantification of RAD51 foci from C as described in Figure 2B.
(E) Cell-cycle analysis via flow cytometry of propidium iodide (PI) stained LNCaP-shPRMT5 cells with (Dox+) and without (Dox−) PRMT5 knockdown.
(F) Cell cycle analysis via flow cytometry of PI-stained LNCaP-shPRMT5 cells 24 h post 2 Gy IR, with (Dox+) and without (Dox−) PRMT5 knockdown.
(G) RNA-seq analysis 1 h post 2 Gy IR in irradiated (IR+) and non-irradiated (IR−) LNCaP-shPRMT5 cells with (Dox+) and without (Dox−) PRMT5 knockdown. Volcano plot shows statistical significance (false discovery rate, FDR-corrected p values) vs fold change (FC, in logarithm scale with base 2) between PRMT5 knockdown and WT in IR+ and IR− cells, respectively. Upregulated DEGs (red or green) and downregulated DEGs (blue or yellow) are indicated in color.
(H) Venn diagram indicating the overlap of DEGs between IR+ (red or blue) and IR− (green or yellow) samples.
(I) Gene ontology (GO) analysis of IR+ only DEGs that were downregulated upon PRMT5 knockdown. Groups of GO terms related to DNA repair and cell-cycle regulation were identified to be significantly enriched in the DEG set. The height of each bar represents the enrichment score for the GO term, whereas the q-value (FDR-corrected p value) in red indicates the significance of enrichment. The number in the bar indicates the number of DEGs associated with the corresponding GO annotation.
(J) Differentially regulated pathways of IR+ only DEGs that were downregulated upon PRMT5 knockdown identified by IPA. The pathways with the highest –log (p value), represented by the bars, are shown. Pathways shown in blue (negative Z score) are inhibited upon PRMT5 knockdown, whereas pathways in orange (positive Z score) are activated upon PRMT5 knockdown.
Fluorescence images in A and C are representative immunocytochemistry images (blue = DAPI, green = Ku70, red = RAD51). Bars in B and D are the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments, whereas bars in E and F are the mean ± s.d. of four independent experiments. Graphs in E and F are representative flow traces of cells in various cell-cycle stages (green = G1, orange = S, blue = G2). Statistical analysis comparing experimental with the control (“Dox−”) was performed using Welch's t test (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001, NS p > 0.05).