Figure 5.
pICln is Also Required for Transcriptional Activation of DDR Genes and for Efficient Repair of DSBs
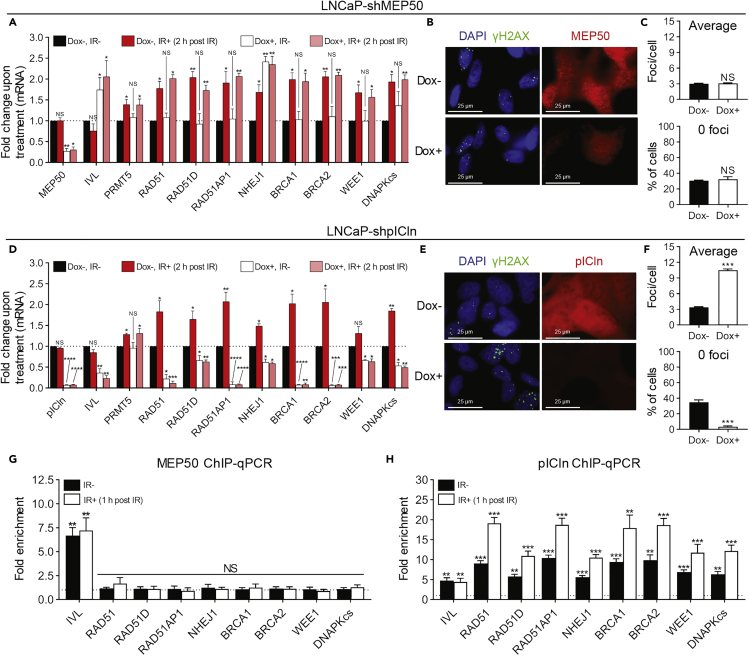
(A) Quantification of mRNA via RT-qPCR 2 h post 2 Gy IR in LNCaP-shMEP50 cells with (Dox+) and without (Dox−) MEP50 knockdown. For each biological replicate, values were normalized to the value for “‘Dox−, IR−” (untreated) to calculate the fold change in mRNA expression upon treatment.
(B) DSBs 6 h post 2 Gy IR in LNCaP-shMEP50 cells with (Dox+) and without (Dox−) MEP50 knockdown.
(C) Quantification of DSBs in each individual cell from B as described in Figure 2B.
(D) Quantification of mRNA via RT-qPCR 2 h post 2 Gy IR in LNCaP-shpICln cells with (Dox+) and without (Dox−) pICln knockdown. For each biological replicate, values were normalized to the value for “Dox−, IR−” (untreated) to calculate the fold change in mRNA expression upon treatment.
(E) DSBs 6 h post 2 Gy IR in LNCaP-shpICln cells with (Dox+) and without (Dox−) pICln knockdown.
(F) Quantification of DSBs in each individual cell from E as described in Figure 2B.
(G and H) Quantification of enrichment (G: MEP50 and H: pICln) at the promoter region of the indicated genes 1 h post 2 Gy IR via ChIP-qPCR in irradiated (IR+) and non-irradiated (IR−) LNCaP-shSC cells via ChIP-qPCR. For each biological replicate, the value for IP was normalized to the value for IgG to calculate the fold enrichment (see also Figures S5E and S5F).
Fluorescence images in B and E are representative immunocytochemistry images (blue = DAPI, green = γH2AX, red = MEP50 or pICln). All bars are the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis for A and D comparing experimental with the control (“Dox−, IR−”) was performed using Brown-Forsythe and Welch ANOVA followed by Dunnett's T3 multiple comparisons test, whereas statistical analysis for C, F, G, and H comparing experimental with the control (“Dox−” or “IgG”) was performed using Welch's t test (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001, NS p > 0.05).