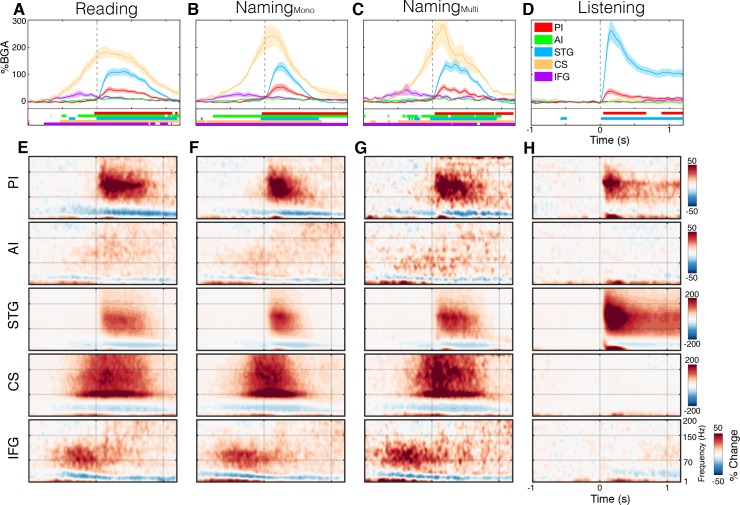
Figure 2. Spectrotemporal representations of activity in the ROIs.
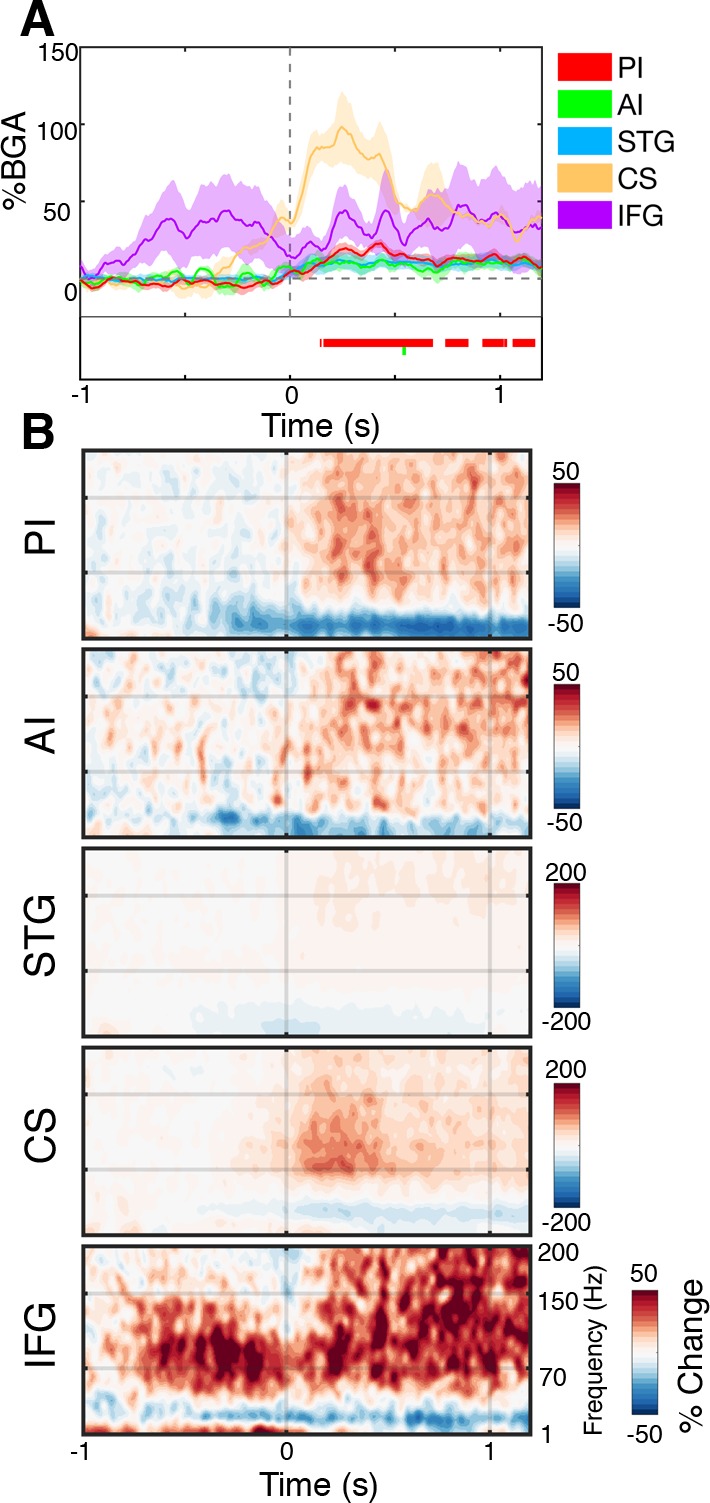
Broadband gamma activity (A–D) and spectrogram (E–H) plots of activity within each ROI, averaged across subjects during the complex reading (A,E; n = 27), monosyllabic naming (B,F; n = 23), multisyllabic naming (C,G; n = 23) and listening (D,H; n = 21) tasks. Colored bars under the BGA plots represent regions of significant activation (q < 0.05). Responses are time locked to speech onset in the reading and naming tasks and to the stimulus onset in listening.
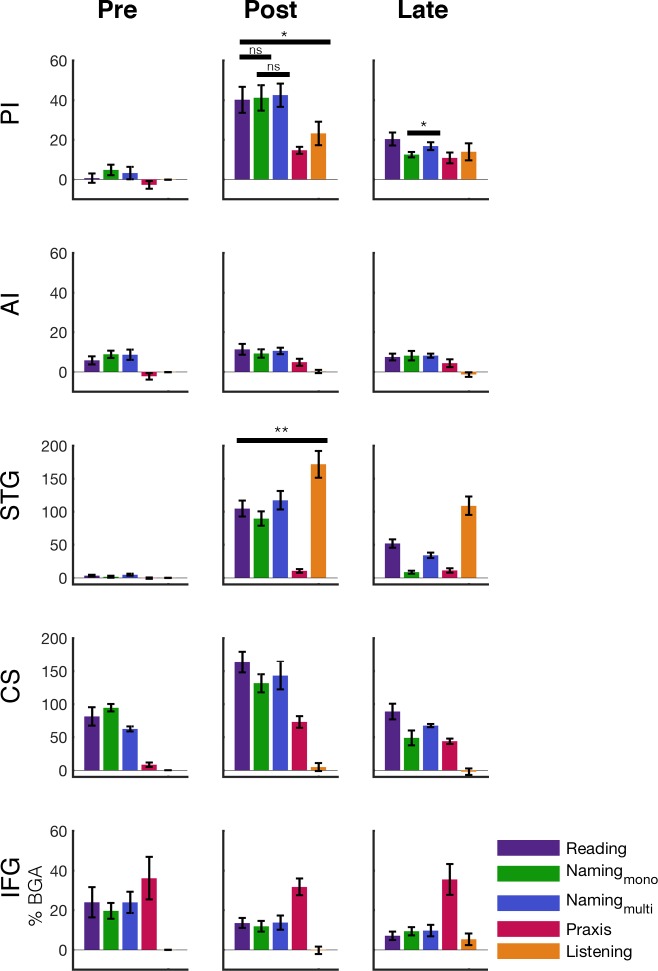
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Time windowed analysis of activity in the ROIs.
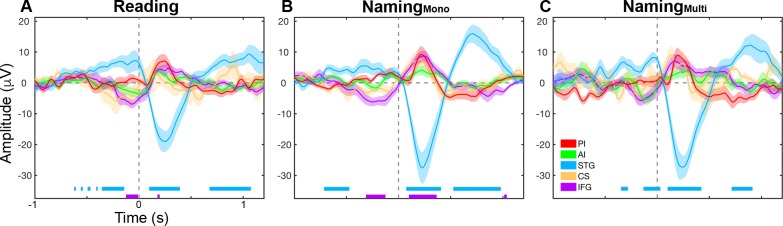
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Spectrotemporal representations of activity in the praxis task.