Fig. 2. Citrus PMFE exhibits robust metabolic protection in HFD-fed mice.
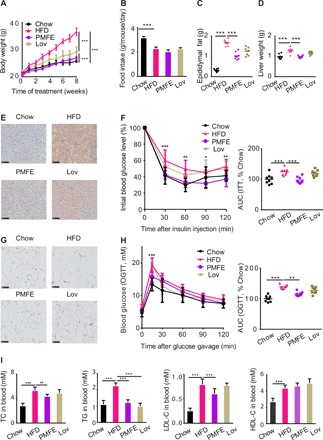
Mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 8). Chow-fed mice were treated daily with 0.5% CMCNa suspension (Chow). HFD-fed mice were orally administrated 0.5% CMCNa suspension (HFD), PMFE (PMFE; 120 mg/kg per day), or lovastatin (Lov; 30 mg/kg per day). (A) Body weight of the chow- and HFD-fed mice treated daily with solvent (0.5% CMCNa), PMFE, or lovastatin for 8 weeks. (B) Average daily food intake for the above four groups of mice. (C) Epididymal fat. (D) Liver weight. (E) Liver lipid content was assessed using oil red O staining (scale bar, 100 μm). (F) Effect of PMFE on percentage of initial blood glucose level during insulin tolerance test (ITT). Right: Area under the curve (AUC). (G) Representative pictures of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)–stained white adipose tissue (scale bar, 100 μm). (H) Effect of PMFE on glucose tolerance measured by oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). Right: AUC. The PMFE-gavaged mice had significantly lower serum glucose levels compared to HFD mice [two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)]. (I) Total TC, TG, LDL, and HDL levels in blood. Error bars are expressed as means ± SD. Statistical significance was determined by one-way or two-way ANOVA with Tukey tests for multiple-group comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
