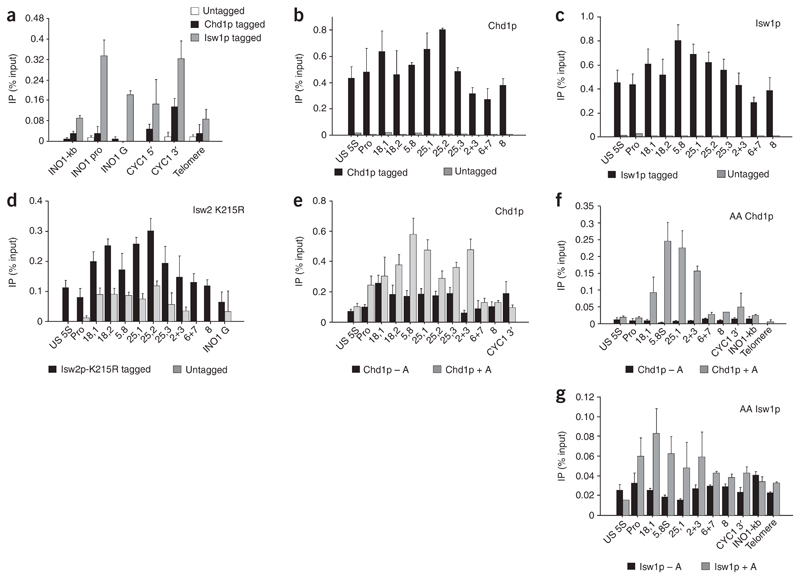
Figure 3. Chromatin-remodeling factors are associated with the entire rDNA repeat.
(a) ChIP analysis of Chd1p and Isw1p over Pol II gene loci (INO1 and CYC1) and telomere DNA showing accumulation of signal from CYC1 3′ probe6. For details of ChIP PCR primers used, see Figure 1a. (b) ChIP analysis of Chd1p across the rDNA repeat in the Chd1p-Myc strain compared with an untagged isogenic control strain. Chd1p is found across the entire repeat, with higher levels seen over genic regions (18,1 to 25,2). Appreciable abundances of Chd1p are also maintained over the termination region and into the spacer region. (c) ChIP analysis of Isw1p across the rDNA repeat in an Isw1p-Myc strain compared with an untagged isogenic control strain. Isw1p is associated with the entire rDNA repeat. (d) ChIP analysis of Isw2-K215R protein across the rDNA repeat in an Isw2-K215R–Flag strain compared with an untagged isogenic control strain. Isw2p-K215R is also associated with the entire rDNA repeat. (e) RNase A treatment (+A) enhances the Chd1p ChIP signals over the transcribed region, indicating that Chd1p does not interact with rRNA. The increase is probably due to enhanced antibody binding upon clearance of RNA, indicating that Chd1p interacts with actively transcribed repeats. (f,g) Chd1p and Isw1p are associated with active rDNA repeats. RNase A treatment before ChIP enhances signals, especially in Chd1-tagged AA strains, over the transcribed region and early-termination region.