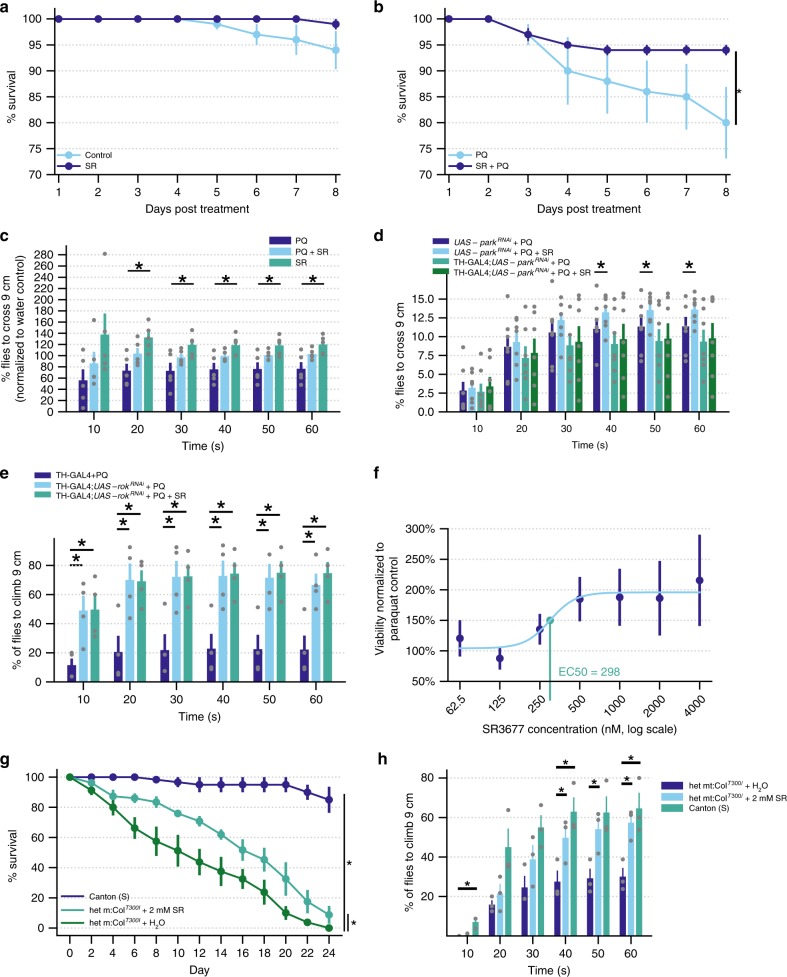
Fig. 6. Survival and climbing impairments arising from genetic and chemical mitochondrial dysfunction are improved by SR3677.
a Seven-day-old male Canton(S) flies were fed water (control), 1 mM SR3677 (SR) (a), 10 mM paraquat (PQ) or paraquat in combination with SR3677 (SR + PQ) (b). The number of flies alive each day was counted (n = 5 independent experiments) and the climbing ability (c) of the flies was assessed (n = 4 independent experiments). d The climbing ability of UAS-parkRNAi and TH-GAL4;UAS-parkRNAi (n = 4 independent experiments), as well as e TH-GAL4 and TH-GAL4;UAS-rokRNAi flies fed paraquat or paraquat co-administered with SR3677 (n = 4 independent experiments). f Cell viability, as indicated by ATP levels normalized to protein concentration of differentiated SH-SY5Y cells co-treated with 500 µM paraquat and the indicated concentrations of SR3677 (n = 4 independent experiments) normalized to control cells treated with paraquat only. g Survival of heteroplasmic mt:ColIT300I flies fed fly food supplemented with water or 2 mM SR3677 and wild-type Canton(S) flies (n = 4 independent experiments). h The climbing ability of heteroplasmic mt:ColIT300I flies fed either water or 2 mM SR3677 for 7 days (n = 3 independent experiments). Log-rank tests were performed to determine P-values for survival analyses (a, b, g), *P < 0.05. P-values were determined by one-tailed paired Student’s t-test for all climbing assays (c–e, h), *P < 0.05. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. All error bars represent s.e.m.