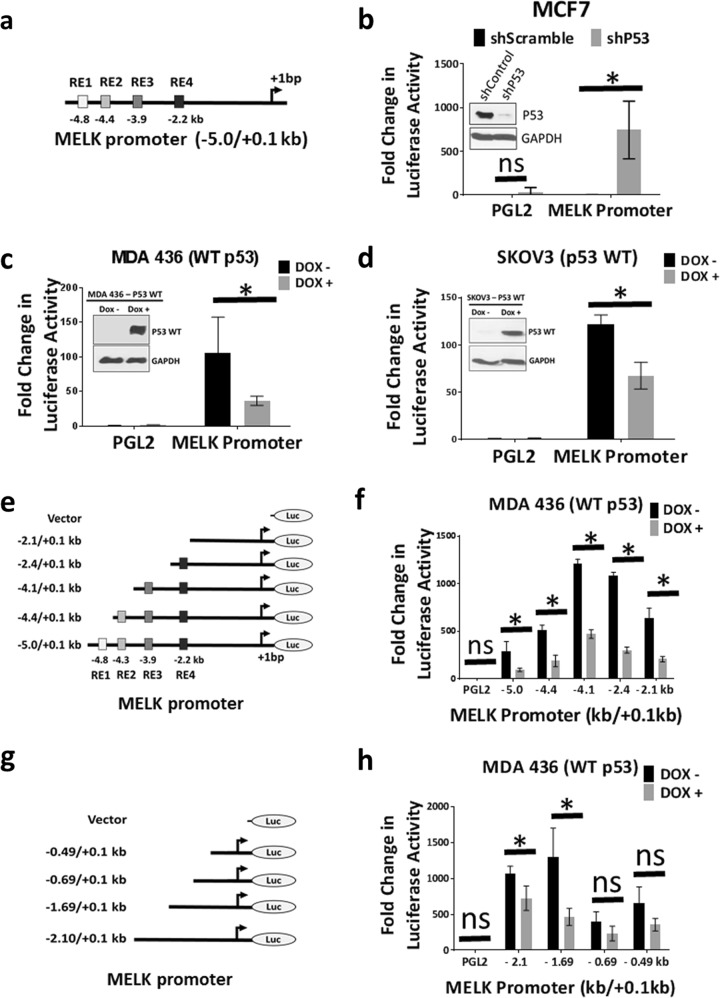
Fig. 4. Inhibition of wild-type p53 elevates MELK promoter activity.
a Schematic diagram of MELK promoter cloned into PGL2-basic luciferase reporter plasmid with predicted p53-binding elements within −5.0 kb. b Luciferase assay to determine MELK promoter activity in MCF7 cells after knocking down of wild-type p53 using shRNA. Inset shows the knockdown of p53. c Luciferase assay to determine MELK promoter activity in p53-null cells (MDA 436) after inducing wild-type p53 expression using doxycycline-inducible system. Inset shows the induction of p53 protein by doxycycline (Dox) treatment. d Luciferase assay to determine MELK promoter activity in p53-null cells (SKOV3) after inducing wild-type p53 expression using doxycycline-inducible system. Inset shows the induction of p53 protein by doxycycline (Dox) treatment. e Schematic diagram of MELK promoter constructs. f Luciferase assay to determine MELK promoter (shown in e) activity in MDA 436 cells after inducing wild-type p53. g Schematic diagram of MELK promoter constructs. h Luciferase assay to determine MELK promoter (shown in g) activity in MDA 436 cells after inducing wild-type p53. For luciferase assays a minimum of three replicates were used. *Statistical significance of p-value < 0.05. Error bars represent ± SD.