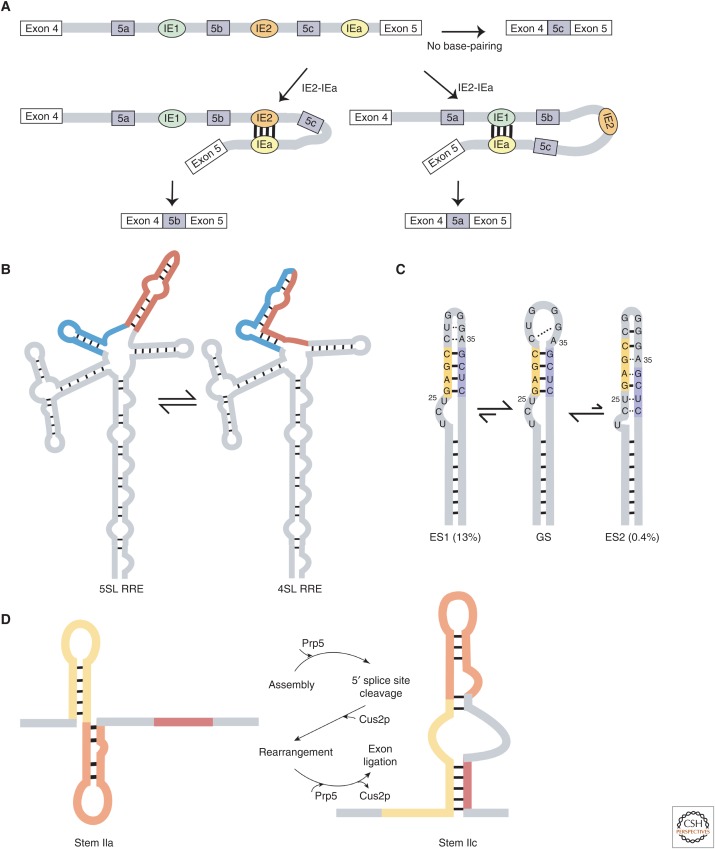
Figure 2.
(A) Mutually exclusive splicing in the 14-3-3ξ mRNA is controlled by three structures that differ in their base-pairing pattern: Intronic element a (IEa) forms base pairs with either IE1 or IE2 or neither. (B) The HIV-1 Rev response element (RRE) partitions into two equally populated structures with either four or five stem loops (SLs). (C) The HIV-1 transactivation response (TAR) element has two “excited” states that differ from the “ground” state (GS). Excited state 1 (ES1) maintains the same overall stem architecture but differs in tertiary interactions at the apical loop, whereas ES2 shows reshuffled base pairs, resulting in a large-scale repairing of the TAR secondary structure. (D) The stem II region on the spliceosome U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) can transition between two alternate conformations that each serve a different role in the process of splicing.