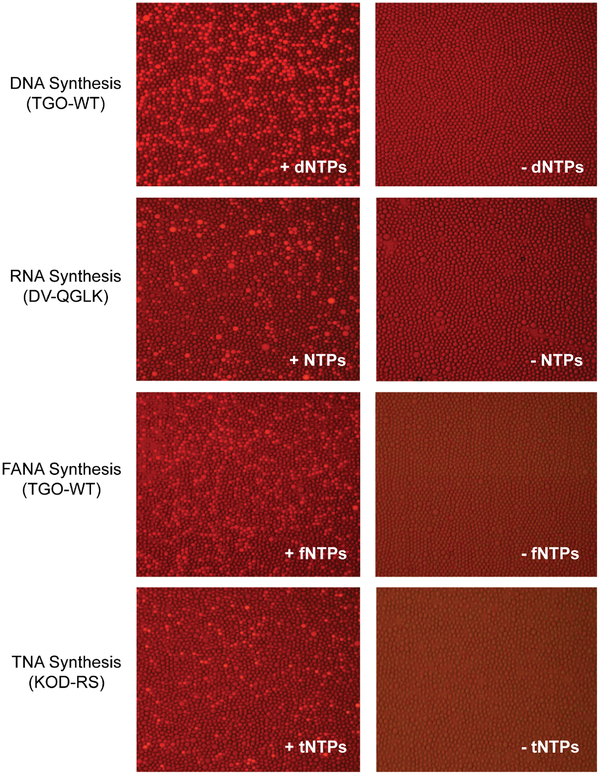
Figure 5. Polymerase-mediated synthesis of natural, non-cognate, and xeno-nucleic acid polymers in uniform droplet microcompartments.
E. coli expressing natural and engineered polymerases were encapsulated in droplet microcompartments, lysed, and assayed for polymerase activity in the presence (left) and absence (right) of the appropriate nucleoside triphosphate. Enzymatic activities include (a) TGO-mediated DNA synthesis; (b) DV-QGLK-mediated RNA synthesis, (c) TGO-WT-mediated FANA synthesis, and (d) KOD-RS-mediated TNA synthesis. The absence of florescence in the no nucleoside triphosphate controls demonstrates that endogenous E. coli nucleotides do not interfere with polymerase activity.