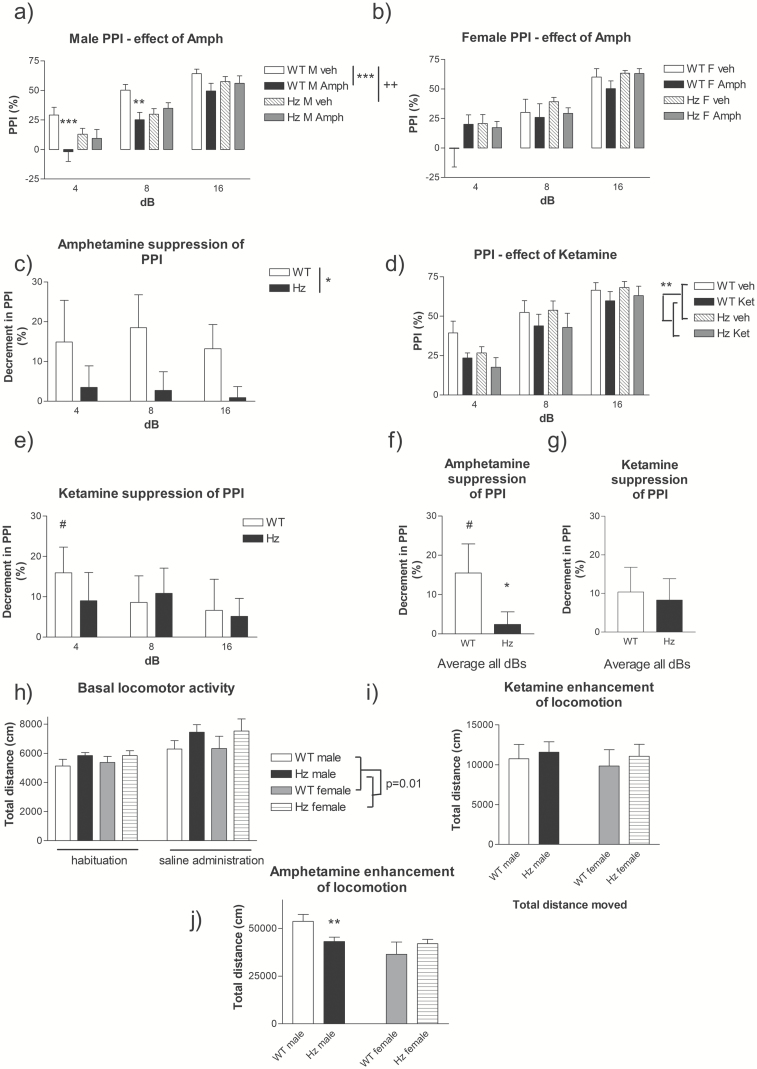
Fig 5.
Analysis of Map2k7+/− mice in behavioral assays relevant to positive symptomatology. PPI in (a) male and (b) female mice following saline or d-amphetamine (5 mg/kg). Males: effect of d-amphetamine (F(1,131) = 14.34, P < .001) and genotype × d-amphetamine (F(1,131) = 14.45, P < .001). Females: no significant effect of d-amphetamine or d-amphetamine × genotype. ** P < .01, *** P < .001 treatment effect (Fisher’s post hoc), ++P < .01 genotype effect. Mean decrement in PPI (vehicle – d-amphetamine) for sex-pooled data (c) separated stimulus dB and (f) pooled dBs. * P < .05 genotype effect ((c) ANOVA, (f) Kruskal–Wallis). (d, e, and g) Ketamine effects on PPI (F(1,95) = 11.30, P < .001) shown as % PPI for pooled-sex mice (d) effect of ketamine (F(1,95) = 11.05, P = .002), genotype × ketamine P = .92. **P < .01 genotype effect. Mean decrement in PPI (vehicle – ketamine) for pooled-sex mice, (e) separated stimulus dB and (g) pooled dBs. (h) Basal LMA during habituation (15 min) and after saline administration (30 min). Map2k7+/− mice showed elevated LMA relative to wild-type (WT) (F(1,39) = 8.3, P = .01). (i) Ketamine (20 mg/kg) induced hyperactivity in both WT and Map2k7+/− mice (F(1,359) = 54.5, P < .001). (j) d-amphetamine (3 mg/kg) also induced hyperactivity (F(1,353) = 1763, P < .001, pooled sex), which was significantly attenuated in male Map2k7+/− mice relative to male WTs (**P < .01, Tukey’s post hoc).