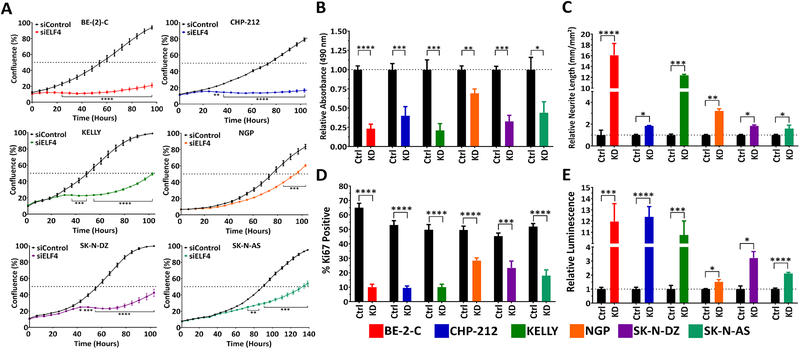
Figure 2. ELF4 is critical for neuroblastoma cell proliferation and reduction of intracellular levels of ELF4 induces differentiation.
(A) Neuroblastoma cell lines were reverse transfected with siRNAs (siELF4 and control) and their proliferation was monitored by live-cell imaging (IncuCyte). (B) Knockdown of ELF4 with siRNA results in a significant decrease in number of viable cells (MTS assay, 120 h post-transfection). (C) Silencing of ELF4 results in differentiation (neurite outgrowth, 120 h post-transfection). (D) ELF4 knockdown significantly diminishes the percentage of Ki67 positive cells (Ki67 quantification, 120 h post-transfection). (E) Loss of ELF4 induces apoptosis (Caspase-3/−7 assay, 48 h post-transfection). Statistical significance of observed differences was determined by Student’s t-test. Proliferation data was adjusted for multiple testing using a Bonferroni correction. * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.01, *** = p<0.001, **** = p<0.0001.