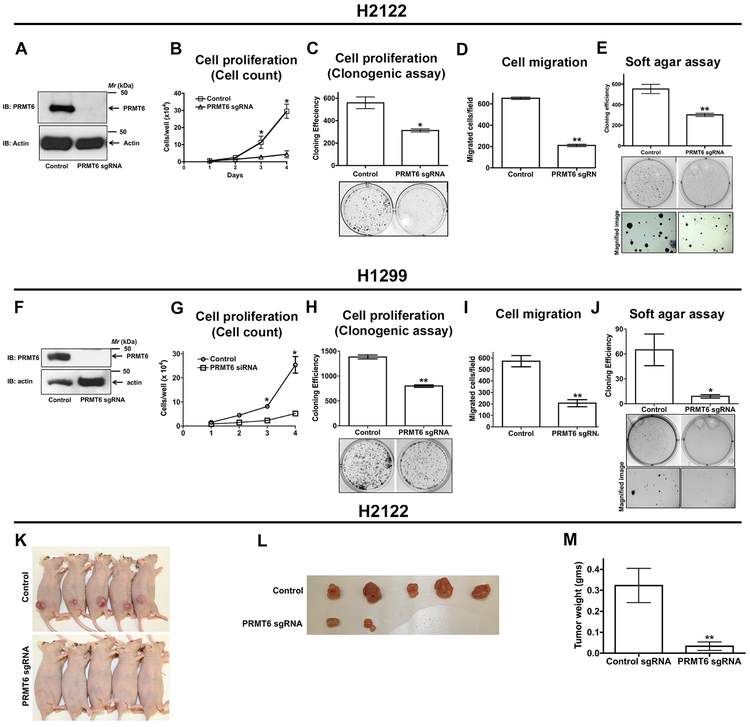
Figure 3: PRMT6 is required for NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, and anchorage-independent growth.
H2122 (A-E) and H1299 (F-J) NSCLC cells were transfected with PRMT6 single guide RNAs (sgRNA), followed by limited dilutions to develop PRMT6 knockout H2122 and H1299 clones. A, F. Lysates of H2122 (A) and H1299 (F) PRMT6 knockout clones and their parental cells were immunoblotted with anti-PRMT6 antibodies. The proliferation rates of H2122 and H1299 PRMT6 knockout clones were determined by hematocytometer cell count (B, G) and clonogenic (C, H) cell proliferation assays as described in the methods. Data represents mean ± SEM from 3 independent highly reproducible experiments. *, p< 0.05; versus parental control. Cell migration rates of H2122 (D) and H1299 (I) PRMT6 knockout clones were assayed in transwell inserts as described in the methods. *, p< 0.05; versus parental control. Anchorage-independent growth of H2122 (E) and H1299 (J) PRMT6 knockout clones were assayed in soft-agars as described in the methods. *, p< 0.05; versus parental control. K-M. H2122 parental cells and PRMT6 knockout H2122 cells were subcutaneously injected into athymic nude mice. Tumor bearing mice (K), extracted tumors (L), and tumor weights (M) were displayed in the figure. **, p< 0.01; versus control.