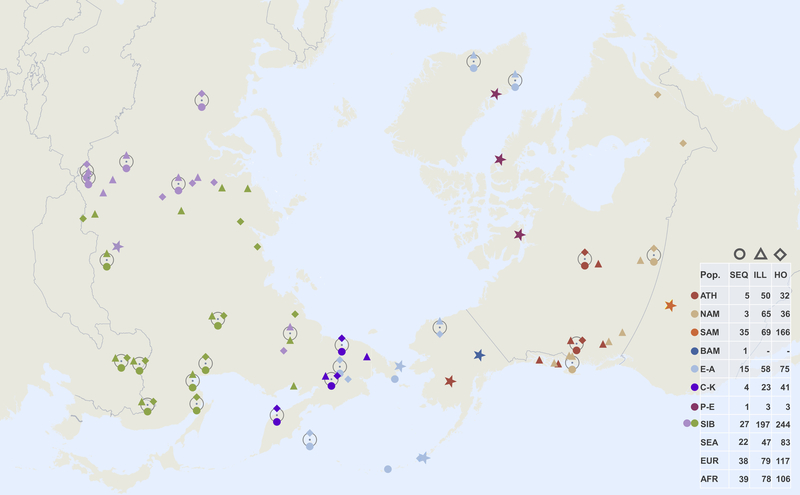
Extended Data Figure 1: Geographic locations of Siberian and North American populations used in this study.
Three main datasets are as follows (Supplementary Tables 4, 5): 1) a set based on the Affymetrix Human Origins genotyping array, including alternatively pseudo-haploid or diploid genotypes for the ancient Saqqaq individual1, diploid genotypes for the ancient Clovis34 individual, together with 1240K SNP capture pseudo-haploid data from six ancient Aleuts who had the highest coverage, two unrelated ancient Athabaskans, 19 ancient Chukotkan Old Bering Sea individuals from the Ekven and Uelen sites, the Middle Dorset and Late Dorset Paleo-Eskimo individuals, and the ancient Ust’-Belaya Angara population of 9 individuals (Supplementary Table 1); 2) a set based on various Illumina arrays, including Saqqaq and the other ancient samples, and 3) a whole genome data set of 190 individuals from 87 populations, including the Saqqaq individual, one ancient Athabaskan individual (I5319), and one ancient Aleut individual (I0719), for which we generated complete genomes with 6.1x and 2.3x coverage, respectively (Supplementary Table 1). The dataset composition, i.e. number of individuals in each meta-population, is shown in the table on the right. Locations of samples with whole genome sequencing data (SEQ) are shown with circles, and those of Illumina (ILL) and HumanOrigins (HO) SNP array samples with triangles and diamonds, respectively. Meta-populations are color-coded in a similar way throughout all figures and designated as follows: Na-Dene speakers (abbreviated as ATH), other northern Native Americans, alternatively named First Peoples (NAM), Southern First Peoples (SAM), Basal First Peoples (BAM), Eskimo-Aleut speakers (E-A), Chukotko-Kamchatkan speakers (C-K), Paleo-Eskimos (P-E), West and East Siberians (WSIB and ESIB), Southeast Asians (SEA), Europeans (EUR), and Africans (AFR). Locations of the Saqqaq, Dorset and other ancient samples are shown as stars colored to reflect their meta-population affiliation.