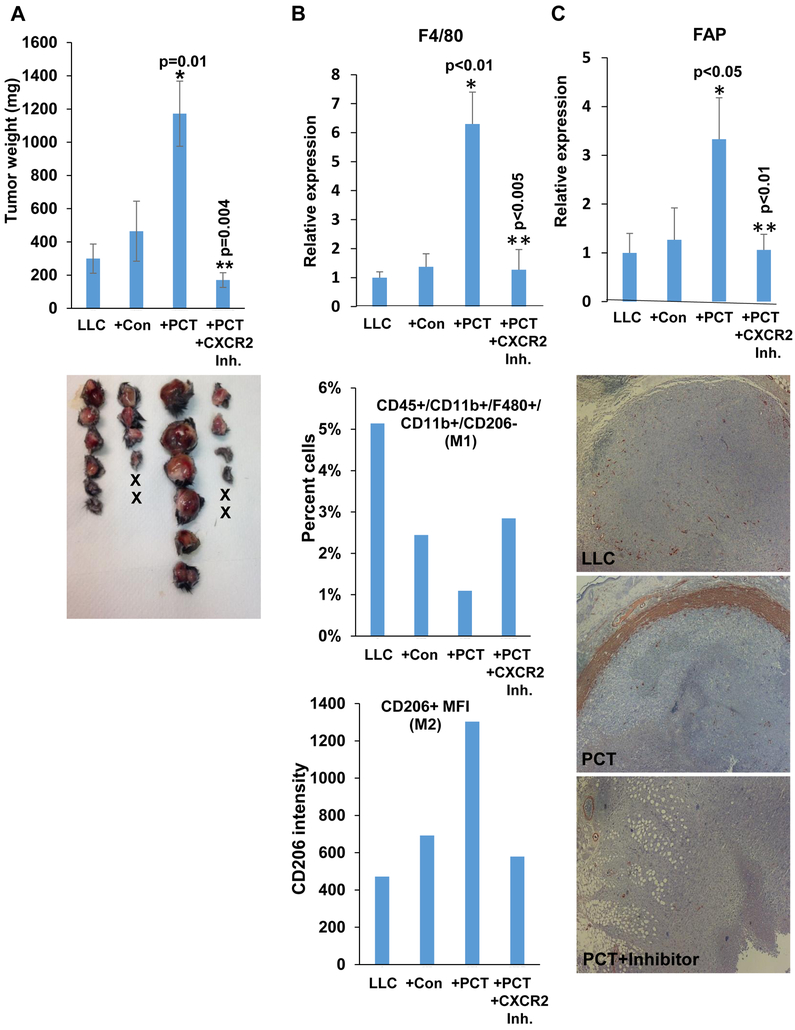
Figure 4.
Enhanced tumor growth by PCT-treated macrophages is mediated by CXCR2. A. Tumor growth. LLC cells (4×105) were inoculated subcutaneously in Hpa-KO mice without (LLC; n=6) or with an equal number of untreated (+Con; n=6) or PCT-treated (+PCT; n=6) macrophages. Mice inoculated with LLC and PCT-treated macrophages were treated with SB225002 (1.5 mg/kg, i.p once daily in DMSO), an inhibitor of CXCR2, or control vehicle (DMSO). At termination on day 23, tumors were excised, weighed (upper panel) and photographed (lower panel). *p=0.01 +PCT vs +Con; **p=0.004 +PCT vs +PCT+CXCR2 inhibitor. Total RNA was extracted from a portion of the tumors and subjected to qPCR applying F4/80 specific primers (B, upper panel). *p<0.01+PCT vs. LLC;**p<0.005 +PCT+CXCR2 Inh vs +PCT. Single-cell suspensions of the tumors were subjected to FACS analyses. The ratio of M1-macrophages (i.e., CD45+CD11b+F4/80+CD206−CD11c+) is shown graphically as a percent of the total cell number (B, second panel). Quantification of median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CD206 (M2 macrophages) is shown in B, lower panel. The rest of the tumors were fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin and five-micron sections were subjected to immunostaining applying anti-SMA antibody (C, lower panels). Original magnifications: x25. qPCR of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) alpha is shown in C, upper panel. *p<0.05 +PCT vs. LLC;**p<0.01 +PCT+CXCR2 Inh vs +PCT.