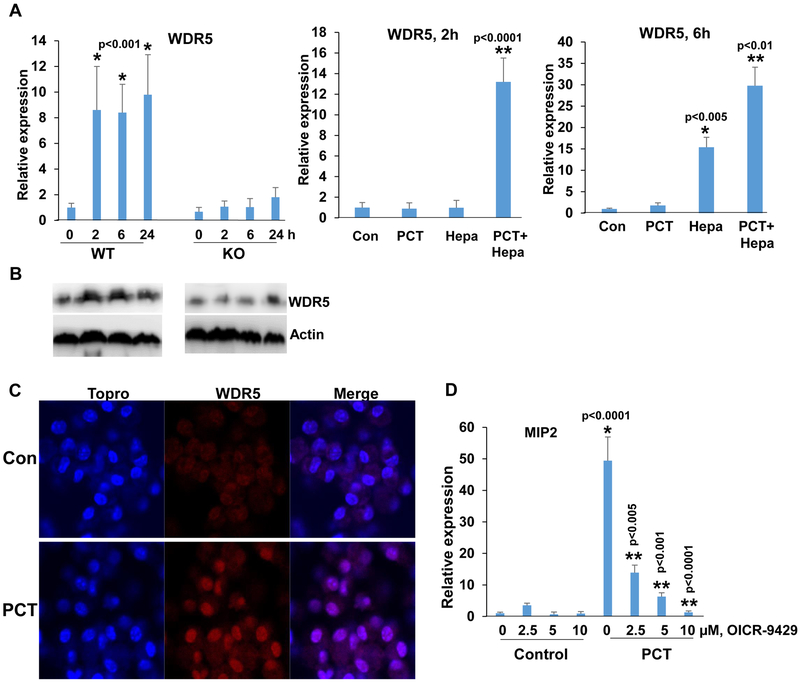
Figure 6.
WDR5 expression by PCT is heparanase-dependent. A. qPCR. Peritoneal macrophages were isolated from WT and Hpa-KO mice and were left untreated (0) or were treated with PCT (15 μg/ml) for the time indicated. Total RNA was then extracted and subjected to qPCR analysis applying primers specific for WDR5 (left panel). *p<0.001 vs control (0). Protein lysates were prepared from corresponding cultures and were subjected to immunoblotting applying anti-WDR5 (upper panels) and anti-actin (lower panels) antibodies (B). Hpa-KO macrophages were left untreated (Con) or were treated with PCT (15 μg/ml), heparanase (Hepa; 1 μg/ml), or both. Total RNA was extracted after 2 (A, middle panel) and 6 (A, right panel) hours, and WDR5 expression was quantified. *p<0.005 Hepa vs. Con; **p<0.01 PCT+Hepa vs Hepa. C. Immunofluorescent staining. Peritoneal macrophages were isolated from WT mice and were left untreated (Con) or were treated with PCT (15 μg/ml) for 24 h. Macrophages were then fixed and permeabilized with methanol, followed by immunofluorescent staining applying anti-WDR5 antibody (middle panels, red); Nuclear (ToPro) staining is shown in blue. D. Peritoneal macrophages were isolated from WT mice and were left untreated (Con) or were treated with PCT (15 μg/ml) in the absence (0) or the indicated concentrations of OICR-9429, a WDR5 inhibitor. DMSO was added as vehicle control (0). Total RNA was extracted after 24 hours and was subjected to qPCR applying primers specific for MIP2. *p<0.001 PCT vs. Con;**p<0.005 PCT+OICR-9429 vs PCT.