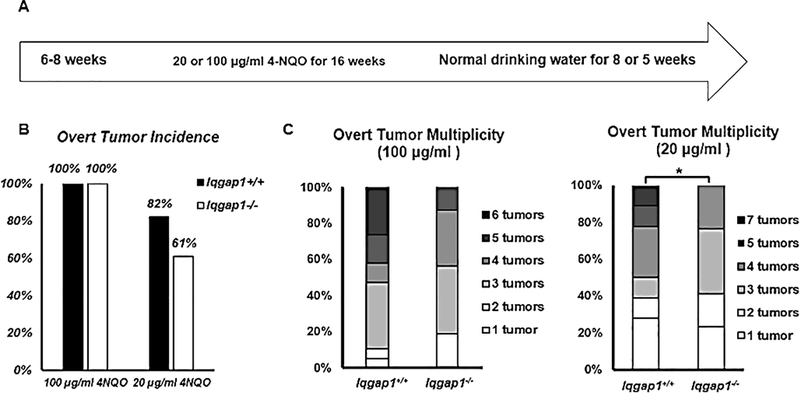
Figure 2. IQGAP1 contributes to head and neck tumorigenesis in vivo.
A) Treatment regimen of 4NQO, a synthetic oral carcinogen. Two dosages of 4NQO were given to mice. In 100 μg/ml treatment, groups of Iqgap1+/+ (n=19) and Iqgap1−/− (n=16) mice were given 100 μg/ml 4NQO in their drinking water for 16 weeks, followed by 5 weeks of normal drinking water. In 20 μg/ml treatment, groups of Iqgap1+/+ (n=22) and Iqgap1−/− (n=28) mice were given 20 μg/ml 4NQO in their drinking water for 16 weeks, followed by 8 weeks of normal drinking water. B) Overt tumor incidence. With 20 μg/ml 4NQO treatment, over tumor incidence in Iqgap1+/+ mice vs. Iqgap1−/− mice not statistically significant (p=0.13, Fisher’s exact test, two-sided). C) Overt tumor multiplicity. With 100 μg/ml 4NQO treatment, Iqgap1+/+ vs. Iqgap1−/−, mean: 3.95 vs. 3.37, p=0.29, Wilcoxon rank sum test, two-sided; with 20 μg/ml 4NQO treatment, Iqgap1+/+ vs. Iqgap1−/−, mean: 2.68 vs. 1.57, p=0.05, Wilcoxon rank sum test, two-sided.