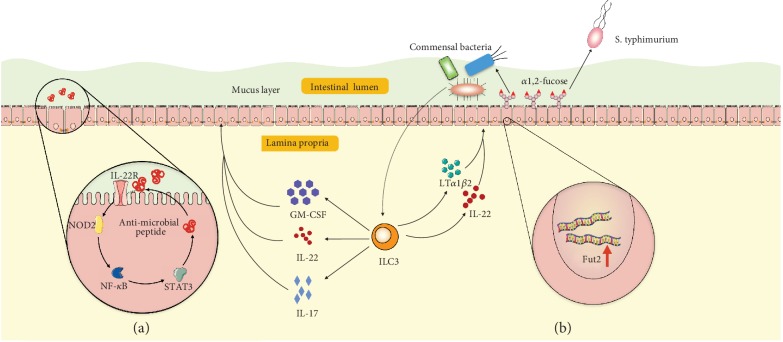
Figure 4.
Illustration of epithelial cells and ILC3 interactions. (a) After bacterial infection, ILC3-derived GM-CSF, IL-22, and IL-17 stimulate epithelial cells by activating the IL-22R-NOD2-NF-κB signaling pathway and result in epithelial cells secreting antimicrobial peptides into the mucus layer. (b) ILC3-derived IL-22 and lymphotoxin (LTα1β2) induce fucosyltransferase 2 (Fut2) gene expression in epithelial cells and result in fucose production in the intestinal tract. Fucose can be utilized by commensal bacteria but not by pathological bacteria such as Salmonella typhimurium. ILC: innate lymphoid cell; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; NOD2: nucleotide oligomerization domain-containing protein 2; NF-κB: nuclear factor- (NF-) κB; STAT3: signal transducers and activators of transcription 3.