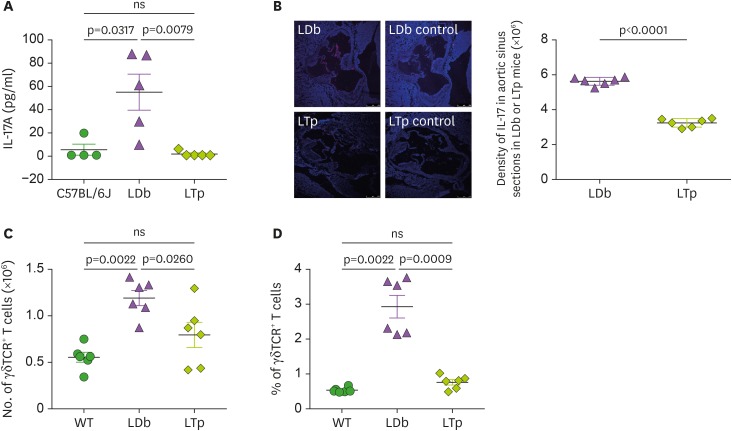
Figure 3. The effect of PCSK9 on IL-17 in C57BL/6J (WT), LDb and LTp mice.
(A) LTp mice had barely detectable plasma levels of IL-17. IL-17 levels in serum obtained from C57BL/6J (n=4), LDb (n=5), and LTp (n=5) mice were measured by ELISA and expressed as pg/ml. (B) LTp mice had barely detectable expression of IL-17 in the aortic sinus. Aortic sinus sections obtained from LDb (n=6) and LTp (n=6) mice were stained with isotype control or polyclonal anti-IL-17 (red) and DAPI (blue). We quantified the intensity of immunofluorescence images expressing IL-17 from each section. LDb mice show increased expression of IL-17 in the aortic sinus, compared to LTp mice. The densities of the expressions of IL17 were determined. (C). LTp mice had decreased numbers of γδTCR+ T cells, compared to LDb mice. The absolute numbers of γδTCR+ T cells in the spleen of WT (C57BL/6J, n=6), LDb (n=6), and LTp (n=6) mice were analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) LTp mice had decreased % of γδTCR+ T cells, compared to LDb mice. The frequency of γδTCR+ T cells in the spleen of WT (C57BL/6J, n=6), LDb (n=6), and LTp (n=6) mice were analyzed by flow cytometry. All results are presented as mean±SD in this figure. Statistical analysis of the esults was performed using 2-tailed unpaired t-tests with Welch's correction. The p values are listed. The p<0.05 is considered significantly.
ns, not significant.