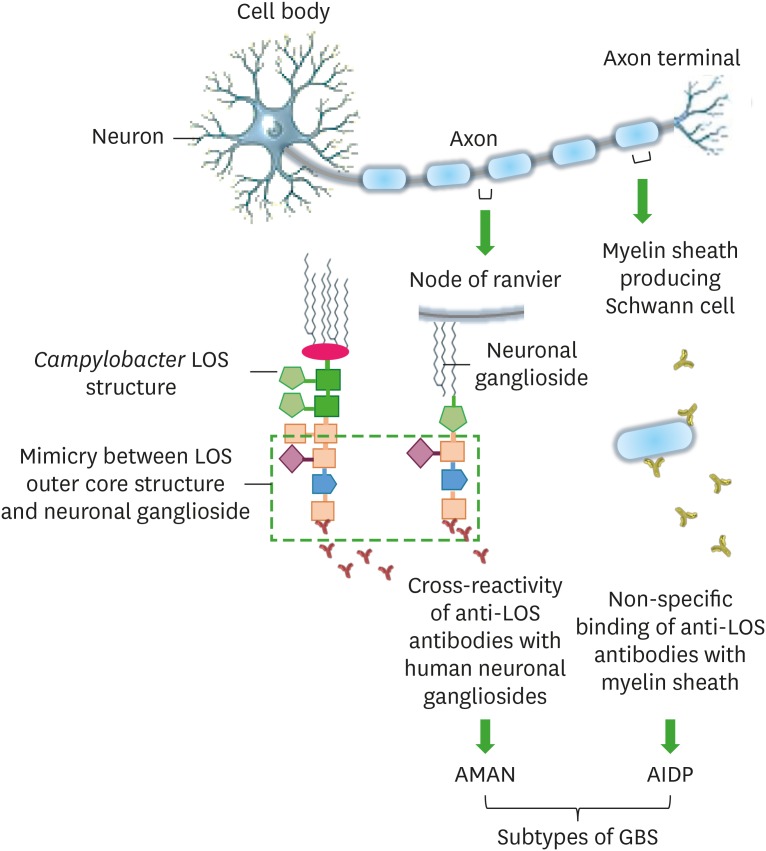
Figure 1. An illustration of interactions of anti-LOS Abs with human neuronal cells, likely to cause GBS in humans post Campylobacter infection.
Cross-reactivity of anti-LOS Abs occurs due to the mimicry between Campylobacter cell surface LOS core structures and human neuronal (node of ranvier) gangliosides and it develops a GBS subtype, AMAN. In some cases, anti-LOS Abs non-specifically bind to the Schwann cells to develop another type of GBS known as AIDP.
AIDP, acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy; AMAN, acute motor axonal neuropathy.