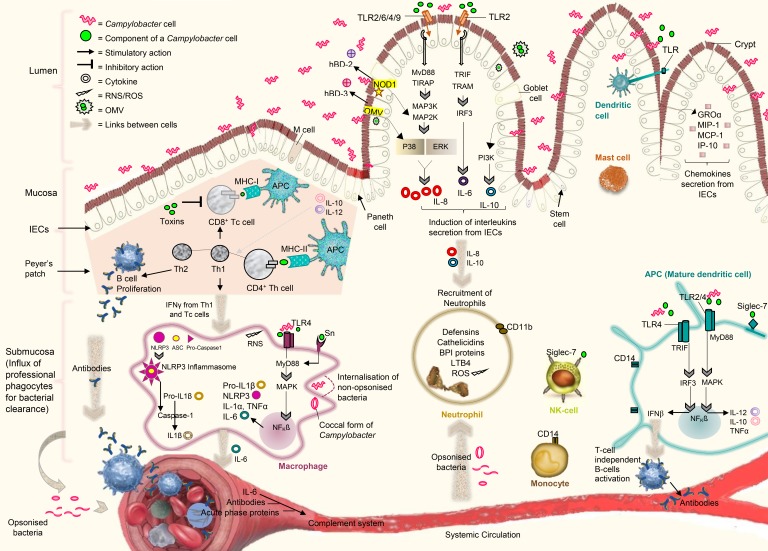
Figure 2. A representation of key immune responses, important for defense in humans against Campylobacter infection. The MyD88 dependent and independent signalling pathways downstream the IECs TLRs are involved in the synthesis of interleukins and chemokines via coordination with NF-κB. The cytosolic receptors (NOD1) and OMV also contribute to the activation of NF-κB for the synthesis of β-defensins. IECs-derived cytokines recruit neutrophils, macrophages, NK cells, and dendritic cells into the intestinal submucosa. The stimulation of MyD88 dependent and independent signalling downstream the TLRs in dendritic cells lead to the secretion of different cytokines, which further activate B-cells in a T-cell independent manner. The activation of MyD88 dependent signalling downstream the cell-surface receptors (TLRs and Sn) and stimulation of cytosolic receptors (NLRP3 inflammasomes) occur in macrophages during Campylobacter infection in order to produce inflammatory cytokines. The mature dendritic cells present Ags by MHC type molecules and secrete interleukins (IL-10 and IL-12) to increase the proliferation of naïve T-cells into Tc and Th cells. The interaction of dendritic expressed siglec-7 with Campylobacter LOS promote the differentiation of Th cells into Th1 and Th2. T-cells activate B-cells to produce Abs specific to the Campylobacter cell constituents. Abs from B-cells, IL-6 from macrophages and high level of acute-phase proteins in serum contribute to the activation of complement systems. Cells are associated to each other by a complex network of cytokines to regulate the immune responses. Cell-to-cell association is demonstrated by large brown arrows.
ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; BPI, bactericidal permeability increasing; GROα, growth related oncogene alpha; IP-10, IFN-γ-inducible protein 10; MAP2K, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases; MAP3K, mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; Sn, sialoadhesin; TIRAP, Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adapter protein.