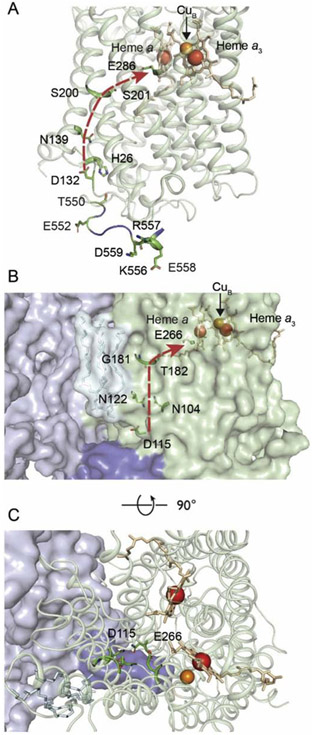
Figure 1. The R. sphaeroides (A) and M. smegmatis (B, C) A1-type CytcOs.
(A) Membrane view of subunit I of the R. sphaeroides CytcO. Five protonatable residues of the C-terminus (E552-D559) are highlighted. Due to the flexibility of the C-terminus, its last six residues, including the protonatable residues E561, R562 and H566, are missing in the structure. The negatively charged E552 is situated about 10 Å from H26. The D pathway, which starts at D132 and ends at E286, is displayed by the red arrow. (B) Membrane view of subunit CtaD (corresponding to subunit I in R. sphaeroides CytcO) and subunit QcrB in M. smegmatis. A loop (blue), extending from subunit QcrB (light purple) of the cyt. bcc complex forms a "lid" that covers the entry point (D115) of the D pathway. The D pathway (D115 to E266) is shown by the red arrow. (C) Same as in B, but a top view. The figures were prepared using the program PyMOL from the PDB files 1M56 (R. sphaeroides) and 6HWH (M. smegmatis).